A report detailing global estimates of modern slavery was released on Tuesday during the 72nd session of the U.N. General Assembly. (Photo: Lisa Kristine/Global Estimates of Modern Slavery)
New Research Reveals There Are More Than 40 Million Slaves Worldwide
Reports released during the UN General Assembly meetings suggest global leaders need to increase efforts to end modern slavery and child labor
New research reveals that more than 40 million people, primarily women and children, were victims of modern slavery in 2016.
Of the 40.3 million victims of modern slavery last year, 24.9 million were in forced labor and 15.4 million were in forced marriages."Modern slavery occured in every region of the world," according to two reports released on Tuesday during the 72nd session of the United Nations General Assembly, and produced by the U.N.'s International Labor Organization (ILO) and the Walk Free Foundation, in partnership with the International Organization for Migration (IOM).
The studies were commissioned to gain a sense of the global situation as the U.N. works to meet target 8.7 of the sustainable development goals, which aims to "take immediate and effective measures to eradicate" modern slavery and human trafficking, "and by 2025 end child labor in all its forms."
Modern slavery is an umbrella term researchers use to refer to "situations of exploitation that a person cannot refuse or leave because of threats, violence, coercion, deception, and/or abuse of power," including forced labor, debt bondage, and forced marriage.
Among the reports key findings were:
- An estimated 40.3 million men, women, and children were enslaved worldwide.
- 24.9 million were in forced labor, working in the sex industry, on construction sites, at domestic residences, in the agriculture sector, and in factories.
- 15.4 million were "in marriages to which they had not consented," and "enduring a situation that involved having lost their sexual autonomy and often involved providing labor."
- Women and girls accounted for 71 percent of total victims, and 99 percent of those forced to work in the sex industry.
- One in four victims were children, and 21 percent of all victims were children who were sexually exploited.
- Over the past five years, an estimated 89 million people have "experienced some form of modern slavery."
- An estimated 152 million children, or nearly one in 10, remain engaged in child labor.
- Among child laborers, 73 million "are in hazardous work that directly endangers their health, safety, and moral development."
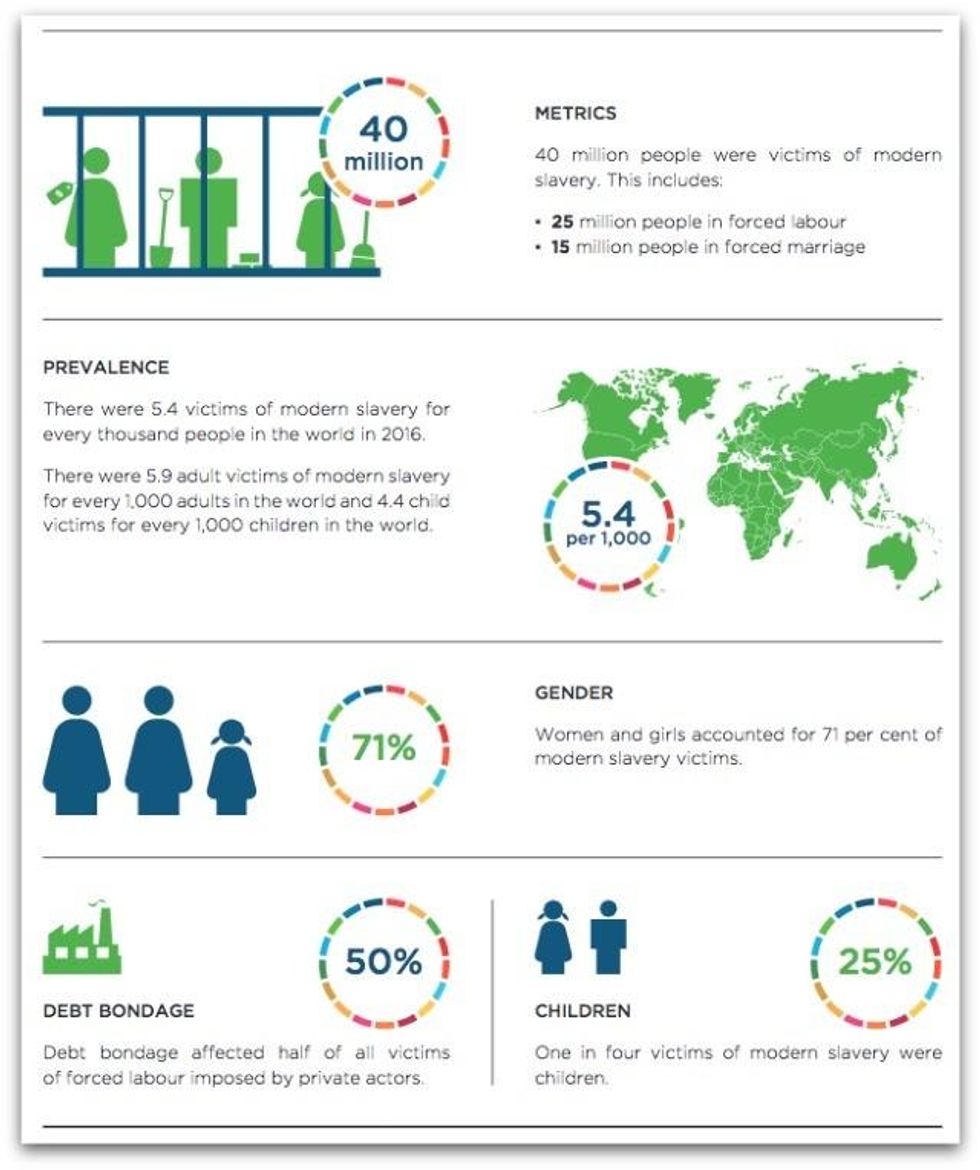
Researchers found that modern slavery was most prevalent in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific, but noted that limited data was available for Arab states and the Americas.
"We believe that the global estimate of 40.3 million is the most reliable data to date, although we believe it to be a conservative estimate as there were millions of people we couldn't reach," Michaelle de Cock, senior statistician at the ILO, told the Guardian. De Cock said those who were unreachable were "in conflict zones, or on the refugee trail, and [in] places where we couldn't be sure of collecting robust data" because of limited access and language barriers.
Even so, Walk Free Foundation's executive director of global research, Fiona David, said, "What is startling about these new estimates is the sheer scale of the modern slave trade." When taking into account that "only 63,000 victims of slavery were reported to the authorities last year," David added, "the gulf between the problem and the insufficient global response becomes very clear."
One report detailed broader findings, while the other focused specifically on child labor. However, both reports emphasized that international cooperation is "imperative," and concluded that "ending modern slavery will require a multi-faceted response that addresses the array of forces--economic, social, cultural, and legal--that contribute to vulnerability and enable abuses."
An Urgent Message From Our Co-Founder
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
New research reveals that more than 40 million people, primarily women and children, were victims of modern slavery in 2016.
Of the 40.3 million victims of modern slavery last year, 24.9 million were in forced labor and 15.4 million were in forced marriages."Modern slavery occured in every region of the world," according to two reports released on Tuesday during the 72nd session of the United Nations General Assembly, and produced by the U.N.'s International Labor Organization (ILO) and the Walk Free Foundation, in partnership with the International Organization for Migration (IOM).
The studies were commissioned to gain a sense of the global situation as the U.N. works to meet target 8.7 of the sustainable development goals, which aims to "take immediate and effective measures to eradicate" modern slavery and human trafficking, "and by 2025 end child labor in all its forms."
Modern slavery is an umbrella term researchers use to refer to "situations of exploitation that a person cannot refuse or leave because of threats, violence, coercion, deception, and/or abuse of power," including forced labor, debt bondage, and forced marriage.
Among the reports key findings were:
- An estimated 40.3 million men, women, and children were enslaved worldwide.
- 24.9 million were in forced labor, working in the sex industry, on construction sites, at domestic residences, in the agriculture sector, and in factories.
- 15.4 million were "in marriages to which they had not consented," and "enduring a situation that involved having lost their sexual autonomy and often involved providing labor."
- Women and girls accounted for 71 percent of total victims, and 99 percent of those forced to work in the sex industry.
- One in four victims were children, and 21 percent of all victims were children who were sexually exploited.
- Over the past five years, an estimated 89 million people have "experienced some form of modern slavery."
- An estimated 152 million children, or nearly one in 10, remain engaged in child labor.
- Among child laborers, 73 million "are in hazardous work that directly endangers their health, safety, and moral development."

Researchers found that modern slavery was most prevalent in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific, but noted that limited data was available for Arab states and the Americas.
"We believe that the global estimate of 40.3 million is the most reliable data to date, although we believe it to be a conservative estimate as there were millions of people we couldn't reach," Michaelle de Cock, senior statistician at the ILO, told the Guardian. De Cock said those who were unreachable were "in conflict zones, or on the refugee trail, and [in] places where we couldn't be sure of collecting robust data" because of limited access and language barriers.
Even so, Walk Free Foundation's executive director of global research, Fiona David, said, "What is startling about these new estimates is the sheer scale of the modern slave trade." When taking into account that "only 63,000 victims of slavery were reported to the authorities last year," David added, "the gulf between the problem and the insufficient global response becomes very clear."
One report detailed broader findings, while the other focused specifically on child labor. However, both reports emphasized that international cooperation is "imperative," and concluded that "ending modern slavery will require a multi-faceted response that addresses the array of forces--economic, social, cultural, and legal--that contribute to vulnerability and enable abuses."
New research reveals that more than 40 million people, primarily women and children, were victims of modern slavery in 2016.
Of the 40.3 million victims of modern slavery last year, 24.9 million were in forced labor and 15.4 million were in forced marriages."Modern slavery occured in every region of the world," according to two reports released on Tuesday during the 72nd session of the United Nations General Assembly, and produced by the U.N.'s International Labor Organization (ILO) and the Walk Free Foundation, in partnership with the International Organization for Migration (IOM).
The studies were commissioned to gain a sense of the global situation as the U.N. works to meet target 8.7 of the sustainable development goals, which aims to "take immediate and effective measures to eradicate" modern slavery and human trafficking, "and by 2025 end child labor in all its forms."
Modern slavery is an umbrella term researchers use to refer to "situations of exploitation that a person cannot refuse or leave because of threats, violence, coercion, deception, and/or abuse of power," including forced labor, debt bondage, and forced marriage.
Among the reports key findings were:
- An estimated 40.3 million men, women, and children were enslaved worldwide.
- 24.9 million were in forced labor, working in the sex industry, on construction sites, at domestic residences, in the agriculture sector, and in factories.
- 15.4 million were "in marriages to which they had not consented," and "enduring a situation that involved having lost their sexual autonomy and often involved providing labor."
- Women and girls accounted for 71 percent of total victims, and 99 percent of those forced to work in the sex industry.
- One in four victims were children, and 21 percent of all victims were children who were sexually exploited.
- Over the past five years, an estimated 89 million people have "experienced some form of modern slavery."
- An estimated 152 million children, or nearly one in 10, remain engaged in child labor.
- Among child laborers, 73 million "are in hazardous work that directly endangers their health, safety, and moral development."

Researchers found that modern slavery was most prevalent in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific, but noted that limited data was available for Arab states and the Americas.
"We believe that the global estimate of 40.3 million is the most reliable data to date, although we believe it to be a conservative estimate as there were millions of people we couldn't reach," Michaelle de Cock, senior statistician at the ILO, told the Guardian. De Cock said those who were unreachable were "in conflict zones, or on the refugee trail, and [in] places where we couldn't be sure of collecting robust data" because of limited access and language barriers.
Even so, Walk Free Foundation's executive director of global research, Fiona David, said, "What is startling about these new estimates is the sheer scale of the modern slave trade." When taking into account that "only 63,000 victims of slavery were reported to the authorities last year," David added, "the gulf between the problem and the insufficient global response becomes very clear."
One report detailed broader findings, while the other focused specifically on child labor. However, both reports emphasized that international cooperation is "imperative," and concluded that "ending modern slavery will require a multi-faceted response that addresses the array of forces--economic, social, cultural, and legal--that contribute to vulnerability and enable abuses."

