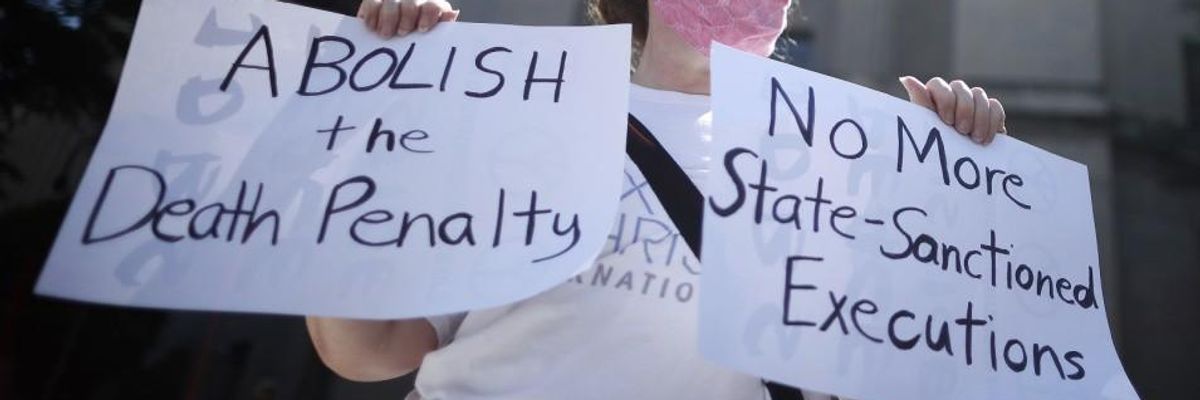
Anti-death penalty activist Judy Coode of Pax Christi International demonstrates in front of the U.S. Justice Department's Robert F. Kennedy Building July 13, 2020 in Washington, D.C.
After Latest US Execution, Progressives Say 'Abolish the Death Penalty'
"The use of the death penalty in the United States is one of the ugliest stains on our broken criminal justice system," said Congresswoman Barbara Lee.
Amid a wave of executions in Republican-led states—including Tuesday's lethal injection of Marcellus Williams in Missouri—progressive U.S. lawmakers and groups renewed calls to "abolish the death penalty."
Congressional Progressive Caucus Chair Pramila Jayapal (D-Wash.) and Congresswomen Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (D-N.Y.), Rashida Tlaib (D-Mich.), Ilhan Omar (D-Minn.), and Cori Bush (D-Mo.) were among those who took to social media to demand an end to capital punishment following Williams' execution.
"The use of the death penalty in the United States is one of the ugliest stains on our broken criminal justice system," said Rep. Barbara Lee (D-Calif.). "It is disproportionately imposed against poor people and people of color. We must abolish it once and for all."
Williams, 55, was killed by the state of Missouri via lethal injection—a method known for botched executions—despite serious doubts about his guilt. The office that prosecuted him sought to have his murder conviction overturned and members of the victim's family pleaded for clemency.
"Sometimes injustice is so glaring that it leaves us struggling to comprehend how such events could happen in the first place," Bush said in a statement released after Williams' execution.
The congresswoman continued:
The deadly decision to execute Williams came despite urgent pleas from Missourians and people all across the country... who called for clemency. Gov. Mike Parson didn't just ignore these pleas and end Williams' life, he demonstrated how the death penalty is wielded without regard for innocence, compassion, equity, or humanity. He showed us how the standard of "beyond a reasonable doubt" can be applied selectively, depending on who stands accused and who stands in power.
"The state of Missouri and our nation's legal system failed Marcellus Williams, and as long as we uphold the death penalty, we continue to perpetuate this depravity—where an innocent person can be killed in the name of justice," Bush stressed. "We have a moral imperative to abolish this racist and inhumane practice, and to work towards building a just legal system that values humanity and compassion over criminalization and violence."
"Rest in power, Marcellus Williams," she added.
Williams wasn't the only one executed on Tuesday. Travis Mullis—a 38-year-old autistic man who murdered his infant son—was killed by lethal injection in Texas after waiving his right to appeal.
Last week, South Carolina executed Freddie Owens by lethal injection after Republican state Attorney General Alan Wilson brushed off a key prosecution witness' bombshell claim that the convicted man did not commit the murder for which his life was taken.
Although the number of U.S. executions has been steadily decreasing from 85 in 2000 to 24 last year, there is currently a surge in state killings, with five more people set to be put to death in three states by October 17.
On Thursday, Alabama is scheduled to kill Alan Eugene Miller using nitrogen gas, despite the inmate suffering severe mental illness. Miller was meant to be put to death in 2022; however, prison staff could not find a vein in which to inject the lethal cocktail and his execution was postponed.
That same day, Emmanuel Antonio Littlejohn is set to be executed by lethal injection in Oklahoma, even after the state's Pardon and Parole Board voted to recommend clemency.
According to a 2014 study, over 4% of people on U.S. death rows did not commit the crime for which they were condemned. The Death Penalty Information Center found that since 1973, at least 200 people who were wrongly convicted and sentenced to death in the U.S. have been exonerated.
"The only way to eliminate the possibility of executing an innocent person is to do away with the death penalty altogether," the advocacy group Human Rights First said Wednesday.
An Urgent Message From Our Co-Founder
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
Amid a wave of executions in Republican-led states—including Tuesday's lethal injection of Marcellus Williams in Missouri—progressive U.S. lawmakers and groups renewed calls to "abolish the death penalty."
Congressional Progressive Caucus Chair Pramila Jayapal (D-Wash.) and Congresswomen Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (D-N.Y.), Rashida Tlaib (D-Mich.), Ilhan Omar (D-Minn.), and Cori Bush (D-Mo.) were among those who took to social media to demand an end to capital punishment following Williams' execution.
"The use of the death penalty in the United States is one of the ugliest stains on our broken criminal justice system," said Rep. Barbara Lee (D-Calif.). "It is disproportionately imposed against poor people and people of color. We must abolish it once and for all."
Williams, 55, was killed by the state of Missouri via lethal injection—a method known for botched executions—despite serious doubts about his guilt. The office that prosecuted him sought to have his murder conviction overturned and members of the victim's family pleaded for clemency.
"Sometimes injustice is so glaring that it leaves us struggling to comprehend how such events could happen in the first place," Bush said in a statement released after Williams' execution.
The congresswoman continued:
The deadly decision to execute Williams came despite urgent pleas from Missourians and people all across the country... who called for clemency. Gov. Mike Parson didn't just ignore these pleas and end Williams' life, he demonstrated how the death penalty is wielded without regard for innocence, compassion, equity, or humanity. He showed us how the standard of "beyond a reasonable doubt" can be applied selectively, depending on who stands accused and who stands in power.
"The state of Missouri and our nation's legal system failed Marcellus Williams, and as long as we uphold the death penalty, we continue to perpetuate this depravity—where an innocent person can be killed in the name of justice," Bush stressed. "We have a moral imperative to abolish this racist and inhumane practice, and to work towards building a just legal system that values humanity and compassion over criminalization and violence."
"Rest in power, Marcellus Williams," she added.
Williams wasn't the only one executed on Tuesday. Travis Mullis—a 38-year-old autistic man who murdered his infant son—was killed by lethal injection in Texas after waiving his right to appeal.
Last week, South Carolina executed Freddie Owens by lethal injection after Republican state Attorney General Alan Wilson brushed off a key prosecution witness' bombshell claim that the convicted man did not commit the murder for which his life was taken.
Although the number of U.S. executions has been steadily decreasing from 85 in 2000 to 24 last year, there is currently a surge in state killings, with five more people set to be put to death in three states by October 17.
On Thursday, Alabama is scheduled to kill Alan Eugene Miller using nitrogen gas, despite the inmate suffering severe mental illness. Miller was meant to be put to death in 2022; however, prison staff could not find a vein in which to inject the lethal cocktail and his execution was postponed.
That same day, Emmanuel Antonio Littlejohn is set to be executed by lethal injection in Oklahoma, even after the state's Pardon and Parole Board voted to recommend clemency.
According to a 2014 study, over 4% of people on U.S. death rows did not commit the crime for which they were condemned. The Death Penalty Information Center found that since 1973, at least 200 people who were wrongly convicted and sentenced to death in the U.S. have been exonerated.
"The only way to eliminate the possibility of executing an innocent person is to do away with the death penalty altogether," the advocacy group Human Rights First said Wednesday.
- Amid Trump Killing Spree, Family of Martin Luther King Jr Joins Chorus Demanding: 'Abolish the Death Penalty' ›
- Amnesty Report Demands Biden Take Action to End Death Penalty ›
- Abolish the Death Penalty and a Touch of Hope for Richard Glossip ›
- UN Experts Urge Biden to Abolish 'Inherently Flawed' Death Penalty ›
- California Halted Executions, Now It Should End the Death Penalty Once and for All ›
- Opinion | From Missouri to Palestine, Where Is Feminism in State-Sanctioned Murder? | Common Dreams ›
- Biden's Hands 'Will Be Bloody' If He Lets Trump Inherit Death Row Cases, Critics Warn | Common Dreams ›
- Amid Global Calls to End Capital Punishment, US Set to Execute 7 Men This Month | Common Dreams ›
- 'Now Imagine... You Are Suffocating': Sotomayor's Graphic Dissent Over Nitrogen Gas Execution | Common Dreams ›
Amid a wave of executions in Republican-led states—including Tuesday's lethal injection of Marcellus Williams in Missouri—progressive U.S. lawmakers and groups renewed calls to "abolish the death penalty."
Congressional Progressive Caucus Chair Pramila Jayapal (D-Wash.) and Congresswomen Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (D-N.Y.), Rashida Tlaib (D-Mich.), Ilhan Omar (D-Minn.), and Cori Bush (D-Mo.) were among those who took to social media to demand an end to capital punishment following Williams' execution.
"The use of the death penalty in the United States is one of the ugliest stains on our broken criminal justice system," said Rep. Barbara Lee (D-Calif.). "It is disproportionately imposed against poor people and people of color. We must abolish it once and for all."
Williams, 55, was killed by the state of Missouri via lethal injection—a method known for botched executions—despite serious doubts about his guilt. The office that prosecuted him sought to have his murder conviction overturned and members of the victim's family pleaded for clemency.
"Sometimes injustice is so glaring that it leaves us struggling to comprehend how such events could happen in the first place," Bush said in a statement released after Williams' execution.
The congresswoman continued:
The deadly decision to execute Williams came despite urgent pleas from Missourians and people all across the country... who called for clemency. Gov. Mike Parson didn't just ignore these pleas and end Williams' life, he demonstrated how the death penalty is wielded without regard for innocence, compassion, equity, or humanity. He showed us how the standard of "beyond a reasonable doubt" can be applied selectively, depending on who stands accused and who stands in power.
"The state of Missouri and our nation's legal system failed Marcellus Williams, and as long as we uphold the death penalty, we continue to perpetuate this depravity—where an innocent person can be killed in the name of justice," Bush stressed. "We have a moral imperative to abolish this racist and inhumane practice, and to work towards building a just legal system that values humanity and compassion over criminalization and violence."
"Rest in power, Marcellus Williams," she added.
Williams wasn't the only one executed on Tuesday. Travis Mullis—a 38-year-old autistic man who murdered his infant son—was killed by lethal injection in Texas after waiving his right to appeal.
Last week, South Carolina executed Freddie Owens by lethal injection after Republican state Attorney General Alan Wilson brushed off a key prosecution witness' bombshell claim that the convicted man did not commit the murder for which his life was taken.
Although the number of U.S. executions has been steadily decreasing from 85 in 2000 to 24 last year, there is currently a surge in state killings, with five more people set to be put to death in three states by October 17.
On Thursday, Alabama is scheduled to kill Alan Eugene Miller using nitrogen gas, despite the inmate suffering severe mental illness. Miller was meant to be put to death in 2022; however, prison staff could not find a vein in which to inject the lethal cocktail and his execution was postponed.
That same day, Emmanuel Antonio Littlejohn is set to be executed by lethal injection in Oklahoma, even after the state's Pardon and Parole Board voted to recommend clemency.
According to a 2014 study, over 4% of people on U.S. death rows did not commit the crime for which they were condemned. The Death Penalty Information Center found that since 1973, at least 200 people who were wrongly convicted and sentenced to death in the U.S. have been exonerated.
"The only way to eliminate the possibility of executing an innocent person is to do away with the death penalty altogether," the advocacy group Human Rights First said Wednesday.
- Amid Trump Killing Spree, Family of Martin Luther King Jr Joins Chorus Demanding: 'Abolish the Death Penalty' ›
- Amnesty Report Demands Biden Take Action to End Death Penalty ›
- Abolish the Death Penalty and a Touch of Hope for Richard Glossip ›
- UN Experts Urge Biden to Abolish 'Inherently Flawed' Death Penalty ›
- California Halted Executions, Now It Should End the Death Penalty Once and for All ›
- Opinion | From Missouri to Palestine, Where Is Feminism in State-Sanctioned Murder? | Common Dreams ›
- Biden's Hands 'Will Be Bloody' If He Lets Trump Inherit Death Row Cases, Critics Warn | Common Dreams ›
- Amid Global Calls to End Capital Punishment, US Set to Execute 7 Men This Month | Common Dreams ›
- 'Now Imagine... You Are Suffocating': Sotomayor's Graphic Dissent Over Nitrogen Gas Execution | Common Dreams ›

