As catastrophic fires ravaged Southern California on Friday, U.S. government scientists confirmed that—as anticipated—2024 was the hottest year on record and the country endured 27 weather and climate disasters with losses exceeding $1 billion.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) found that after 15 straight months of new records from June 2023 through August 2024, global temperatures last year were 2.3°F (1.28°C) above the agency's 20th-century baseline from 1951-1980 and about 2.65°F (1.47°C) higher than the mid-19th century average from 1850-1900.
"Between record-breaking temperatures and wildfires currently threatening our centers and workforce in California, it has never been more important to understand our changing planet."
"Once again, the temperature record has been shattered—2024 was the hottest year since recordkeeping began in 1880," said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson in a statement. "Between record-breaking temperatures and wildfires currently threatening our centers and workforce in California, it has never been more important to understand our changing planet."
Other experts, at NASA and beyond, also responded to the findings by emphasizing that the climate emergency was created by humanity extracting and burning fossil fuels—and continuing to do so, despite scientists' warnings and initiatives including the 2015 Paris agreement, which was intended to limit global temperature rise this century to 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
"To put that in perspective, temperatures during the warm periods on Earth three million years ago—when sea levels were dozens of feet higher than today—were only around 3°C warmer than preindustrial levels," explained Gavin Schmidt, director of NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies. "We are halfway to Pliocene-level warmth in just 150 years."
"Not every year is going to break records, but the long-term trend is clear," said Schmidt, acknowledging natural fluctuations such as El Niño and La Niña. "We're already seeing the impact in extreme rainfall, heatwaves, and increased flood risk, which are going to keep getting worse as long as emissions continue."
NASA noted that independent analyses from Berkeley Earth, Europe's Copernicus Climate Change Service, the United Kingdom's Met Office, and the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) also concluded that "global surface temperatures for 2024 were the highest since modern record-keeping began," though some of the figures differ slightly due their to various methodologies and models.
For example, NOAA, which also released its 2024 conclusions on Friday, found that the global surface temperature was 2.32°F (1.29°C) above the 20th-century average and exceeded the 1850-1900 average by 2.63°F (1.46°C). The agency also found that the annual average for the contiguous United States was 55.5°F—3.5°F above average and the warmest in the 130-year record.
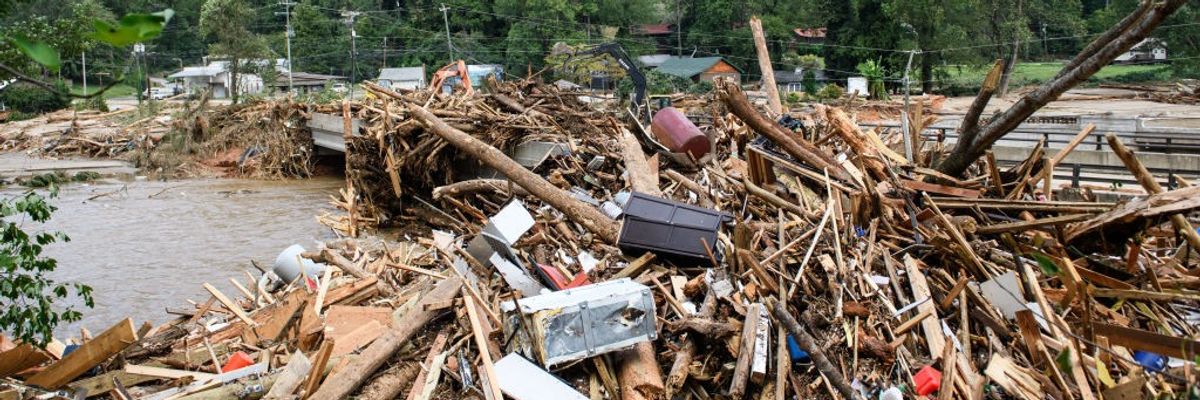
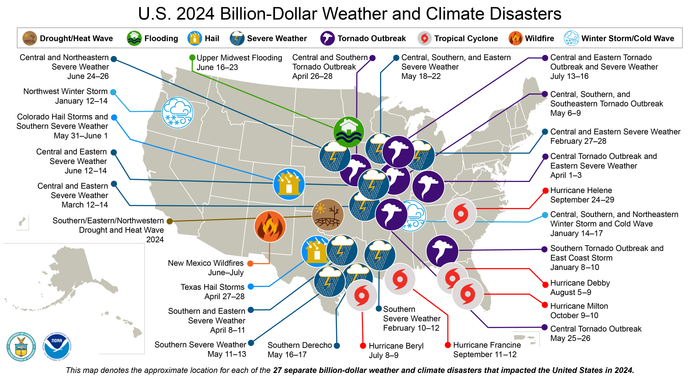
NOAA also put out findings on extreme weather events that are becoming more common and devastating due to fossil fuel-driven global heating. The agency identified 27 disasters across the country—a drought, a flooding event, a wildfire, two winter storms, five tropical cyclones, and 17 severe storms—with losses topping $1 billion each. They collectively cost $182.7 billion and killed at least 568 people.
Over a third of those deaths—219—were tied to Hurricane Helene, last year's costliest event at $78.7 billion. The Category 4 storm made landfall in Florida's Big Bend region and left a trail of destruction up to North Carolina and Tennessee. NOAA said that it "was the deadliest Atlantic hurricane since Maria (2017) and the deadliest to strike the U.S. mainland since Katrina (2005)."
The United States has faced 403 billion-dollar weather and climate disasters over the past 45 years, and 2024 had the second-highest count, after 28 events in 2023. The annual average for 1980-2024 is just nine, compared with 23 for the past five years.
 (Image: NOAA)
(Image: NOAA)
"Last year's record-breaking heat and billion-dollar disasters are an alarming harbinger of what's to come if the nation fails to invest in a climate-resilient economy and do its part to sharply cut global heat-trapping emissions," said Rachel Cleetus, policy director and lead economist at the Union of Concerned Scientists' (UCS) Climate and Energy Program, in a statement. "It's time for decision-makers at all levels of government and across the economy to acknowledge the staggering financial costs and human toll of burning fossil fuels and commit to building a stronger, safer economy powered by clean energy."
Cleetus also called out the fossil fuel companies that "seem intent on burning down the planet to protect their profits" and the "policymakers in their thrall." Her UCS colleague Astrid Caldas, a senior climate scientist for community resilience, similarly stressed the urgent need to act while blasting Big Oil and its allies in politics.
"As a scientist exhausted from sounding the alarm hottest year after hottest year, I'm no longer just concerned about the climate crisis and its impacts on vulnerable communities but incensed at world leaders for their grossly inadequate climate action to date," Caldas declared. "NOAA and NASA confirmed that the last 11 years have been the 11 hottest on record. Will it take another 11 years for policymakers to heed the irrefutable science and address the devastation being experienced in the United States and around the world largely due to fossil-fuel driven global warming?"
As Californians faced what experts fear will be the costliest fire disaster in U.S. history, Caldas said that "deadly and costly climate impacts, including accelerating sea-level rise and record-breaking heatwaves, droughts, storms, and wildfires, are mounting, and yet politicians stand by while heat-trapping emissions continue to rise globally. The science is indisputable: Transformative and comprehensive global climate action, including a speedy and just transition away from fossil fuels and increased investments in climate resilience, is paramount to protect people now and foster prosperity for generations to come."
"The villains of this escalating tragedy are also clear, with wealthy nations, the duplicitous fossil fuel industry, and spineless policymakers topping the list of those bearing primary responsibility for past and current global warming emissions and climate inaction," she added. "The biggest injustice is that the most vulnerable communities on the frontlines of the climate crisis have much to lose despite contributing the least to this problem."


 (Image: NOAA)
(Image: NOAA)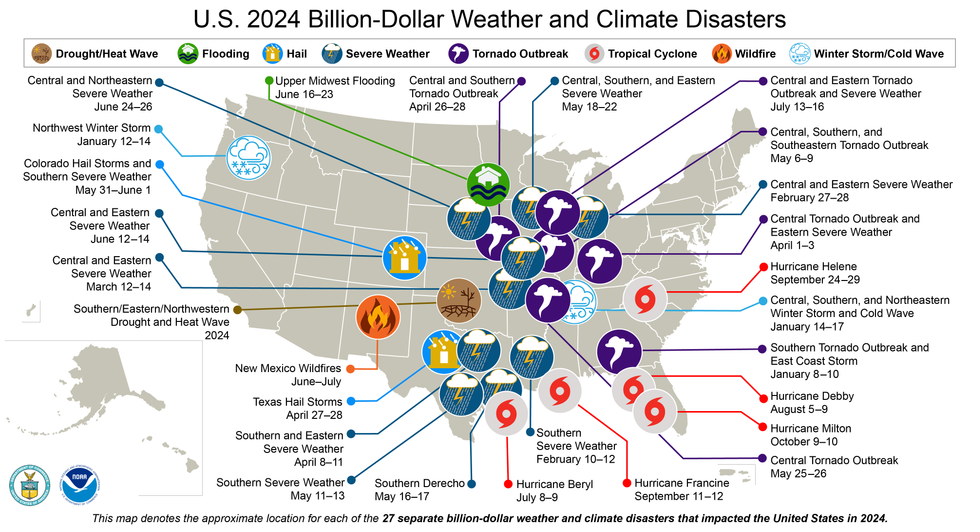 (Image: NOAA)
(Image: NOAA)