March, 17 2013, 01:23pm EDT
The War in Iraq; 10 Years and Counting
IRAQ
The US/UK-led invasion of March 2003 has brought a decade of high and low intensity armed conflict to Iraq. But this conflict is not yet history. It remains entrenched and pervasive, with a clear beginning but no foreseeable end, and very much a part of the present in Iraq. In major regions of the country armed violence continues to exact a remorseless toll on human life, young and old, male and female, across society.
Since the beginning of 2003 the Iraq Body Count project (IBC) has been continuously tracking, analysing and maintaining a public record of civilian deaths on its website iraqbodycount.org.
The figures below provide a statistical overview of the conflict which outlines its human toll. Numbers are derived from over 31,500 deadly incidents analysed for information including time and location, perpetrators and weapons used, with demographic records for those victims (around 40% of the total) for whom such information could be obtained.
IN SUM:
IBC has documented 112,017 - 122,438 civilian deaths from violence between 20 March 2003 and 14 March 2013.
A complete account of violent deaths that includes Iraqi and foreign combatants (including coalition forces), as well as previously unreported civilian deaths still being extracted by IBC from the Iraq War Logs released by WikiLeaks, would include:
+ 39,900 (combatants killed of all nationalities);
+ 11,500 civilians (likely to be added from the Iraq War Logs); yielding about 174,000 as the number of people documented killed in violence in Iraq since 2003.
IBC has recorded an additional 135,089 civilians injured, along with incident and demographic details where known. However IBC only records injured in incidents where there were also deaths, and (unlike for deaths) official Iraqi figures are consistently higher than IBC's. In May 2012 the Iraqi Ministry of Health reported that there had been 250,000 injured since 2003. (See https://aknews.com/en/aknews/3/306941)
IN DETAIL:
The most intense period for civilian deaths was at the war's very beginning, when more than 6,700 were killed in just 3 weeks of 'Shock and Awe' (from 20th March to the seizure of Baghdad on 9th April: a rate of 320 per day for 21 days).
The most violent month after the invasion was July 2006, with 3,266 violent deaths. The most sustained period for high-level violence was during the fourth and fifth years from March 2006 to March 2008, when 'sectarian' killings peaked and some 52,000 died.
Annual civilian deaths since 2003 (counting from 20 March-19 March each year):
- 14,007 in year one
- 12,001 in year two
- 17,026 in year three
- 31,418 in year four
- 20,930 in year five
- 7,829 in year six
- 4,747 in year seven
- 4,133 in year eight
- 4,433 in year nine
- ~4250 in year ten
The majority of civilian deaths during the first year (at least 55%) were directly caused by US/Coalition forces, who were reported as directly causing around 7% of all deaths in the subsequent period until their formal withdrawal on 31st December 2011.
Current deaths per year for civilians in Iraq (at between 4 and 5 thousand) are still of the same order as the total number of US and Coalition military killed over the entire 10 year period (now 4,804 according to https://icasualties.org). Overall there have been 25 Iraqi civilian deaths for every one US and coalition forces death.
Iraqi victims of the war come from all walks of life. IBC was able to determine the occupation of nearly 23,600 victims, covering some 700 professions. By far the greatest number were police who, along with journalists, are also most likely to have their profession mentioned, and hence to have been most completely recorded.
IBC's documented occupational groupings, and the number of deaths reported for each, include:
- 10,238 police (excluding paramilitaries)
- 2,783 neighbourhood and private security
- 1,605 officials and public sector workers
- 751 community and religious leaders
- 288 journalists and media workers
- 265 medics and health care workers
Among slightly more than 50,000 victims about whom IBC could obtain demographic information, men numbered 38,441 (77%), women 4,373 (8.7%), and children 4,191 (8.4%). The weapons that kill women and children tend to be different from those used to kill adult males, who are more often directly or even individually targeted. (For a detailed account of the demographics of victims and the weapons that killed them, see IBC co-authored articles in the New England Journal of Medicine, PLoS Medicine, and Lancet - see Note 3)
During these ten years 41,636 civilians were killed by explosives (including in 13,441 suicide attacks), and a further 5,725 by air attacks (usually also involving explosive munitions), and 64,226 by gunfire. There were 81 very large-scale bomb attacks over the post-invasion period, each claiming on average 85 lives and leaving about 200 wounded (from 6,879 killed, 16,340 wounded). The worst year for these events was 2007, with 20 such incidents, half of them in Baghdad. (For a review of these incidents up to Oct 2007, see https://www.iraqbodycount.org/analysis/numbers/biggest-bombs/)
Baghdad, the country's capital and its political and administrative centre, and also by far its most populous city, has seen the greatest loss of life overall, with 58,252 lives lost (48% of all deaths), and continues to see the largest number of deaths year on year. But when measured against the size of its population, it takes second place to the province of Diyala (capital: Baquba), with civilian violent death rates of 8 per thousand against Diyala's 9 per thousand. Other highly-affected provinces include Anbar (which includes the city of Fallujah) with 6 deaths per thousand and Salah al-Din (capital: Tikrit) with 5 per thousand. Moreover, these last three were the areas with the highest rates of violence (measured against population size) in 2012.
There has been an underlying anti-occupation / anti-government conflict throughout the period, identifiable both by the weapons it uses and its targets, with civilians caught either in the crossfire or targeted for their connection to the government. While deaths generally attributed to sectarian conflict have dropped 10-fold since their height during 2006-2008, deaths linked to anti-government actors have remained roughly steady at around 1,000--3,000 per year throughout, in recent years accounting for around a quarter of deaths (many of these being police).
This anti-government conflict forms a significant part of the violence now entrenched in Iraq, which has shown no diminution in recent years. While military forces were able to bring war to Iraq, it has not left with them.
A proper understanding of the war's human consequences, both past and present, remains to be established. This human question cannot be stated only in terms of numbers. When people die, it is not enough merely to establish how many died but to know who died. This knowledge is taken as a given for coalition soldiers killed, but as far as Iraqi civilian victims are concerned, only a tiny minority of their names or identities are part of the public record.
Of IBC's current total of 122,438 documented civilian deaths, only 8,647 (7%) are even nominally identified. Each has their own page on the IBC website, but the identification of the vast majority is a task for the future, one which will require much broader participation, including from within the Iraqi population.
Iraq Body Count (IBC) is a citizens' initiative devoted to recording the violent civilian deaths that have resulted from the 2003 military intervention in Iraq. Its public database includes deaths caused by US-led coalition forces and paramilitary or criminal attacks by others. The project was founded in January 2003 by volunteers from the UK and USA who felt a responsibility to ensure that the human consequences of military intervention in Iraq were not neglected.
LATEST NEWS
Sanders Gets GOP Leader to Agree to Work On Medicare Covering Dental, Hearing, and Vision
The exchange on the Senate floor came after the Finance Committee chair blocked passage of the Vermont Independent's bill.
Mar 11, 2025
U.S. Senate Finance Committee Chair Mike Crapo on Tuesday blocked passage of Sen. Bernie Sanders' legislation to expand Medicare to cover dental, hearing, and vision care for tens of millions of American seniors, but the bill's sponsor got the panel leader to publicly agree to further discuss the issue.
Sanders (I-Vt.) took to the Senate floor Tuesday afternoon to ask for unanimous consent to pass the Medicare Dental, Hearing, and Vision Expansion Act, which is spearheaded in the House of Representatives by Congressman Lloyd Doggett (D-Texas).
"In the richest country in the history of the world, it is unacceptable that millions of seniors are unable to read because they can't afford eyeglasses, can't have conversations with their grandchildren because they can't afford hearing aids, and have trouble eating because they can't afford dentures," Sanders said in a statement.
"That should not be happening in the United States of America in the year 2025," he continued. "The time is long overdue for Congress to expand Medicare to include comprehensive coverage for the dental, vision, and hearing care that our seniors desperately need."
After Crapo (R-Idaho) rose to stop the bill from advancing, he and Sanders had a brief exchange in which the Republican agreed to working on achieving the "outcome" of the federal healthcare program covering dental, vision, and hearing.
In Sanders' remarks on the Senate floor about his bill, he sounded the alarm about efforts by President Donald Trump, billionaire Elon Musk, and congressional Republicans to cut government healthcare programs and Social Security.
"Yeah, we have more nuclear weapons than any other country, we have more billionaires than any other country, but we also have one of the highest rates of senior poverty of any country on Earth. We might want to get our priorities right," said Sanders, who has long fought for achieving universal healthcare in the United States via his Medicare for All legislation.
"While my Republican colleagues would like to make massive cuts to Medicaid in order to provide more tax breaks to billionaires, some of us have a better idea," he said. "We think that it makes more sense to substantially improve the lives of our nation's seniors by expanding Medicare to cover dental, vision, and hearing benefits."
To pay for his expansion plan, Sanders calls for ensuring that Medicare pays no more for prescription drugs than the Department of Veterans Affairs and addressing the tens of billions of dollars that privately administered Medicare Advantage plans overcharge the federal government annually.
In a statement about the bill, Doggett highlighted that "this expanded care could help prevent cognitive impairment and dementia, worsened chronic disease, and imbalance leading to falls with deadly consequences. This is an essential step to fulfilling the original promise of Medicare—to assure dignity and health for all."
Welcoming their renewed push for Medicare expansion, Public Citizen healthcare advocate Eagan Kemp declared that "at the same time Trump and his cronies in Congress try to rip healthcare away from millions and push for further privatization of Medicare, Sen. Sanders and Rep. Doggett are showing what one of our top priorities in healthcare should be—improving traditional Medicare."
"The introduction of this legislation is an important step to ensure Medicare enrollees can access the care they need, and we hope that Congress will act quickly to pass these commonsense reforms," Kemp added. "Healthcare is a human right."
Earlier Tuesday, in anticipation of Crapo's committee holding a confirmation hearing for Dr. Mehmet Oz, the former television host Trump has nominated to lead the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid, Public Citizen released a research brief about the hundreds of millions of dollars Medicare Advantage companies have spent on lobbying.
"If Oz is confirmed as the CMS administrator," Kemp warned, "attacks on traditional Medicare are likely to move into overdrive."
Keep ReadingShow Less
Trump Lifts Ukraine Aid Pause After Kyiv Agrees to Cease-Fire Proposal
Ukraine's foreign minister called the endorsement a "step that proves Ukraine is ready to move forward on the path to a just end to the war."
Mar 11, 2025
The Trump administration said Tuesday that it would resume military aid to and intelligence-sharing with Ukraine after that country's leadership endorsed a U.S. proposal for a 30-day cease-fire in the war defending against Russia's three-year invasion and occupation.
The Washington Postreports that U.S., Ukrainian, and Saudi officials met for eight hours on Tuesday in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. No Russian officials were present at the negotiations.
"We're going to tell them this is what's on the table. Ukraine is ready to stop shooting and start talking," U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio said after the meeting. "And now it'll be up to them to say yes or no. If they say no, then we'll unfortunately know what the impediment is to peace here."
Ukraine has agreed to a 30 day ceasefire. Incredible work by Trump team. Now if Russia agrees, Trump may have gotten cease fires in the Middle East and Europe in his first 60 days. Nobel Peace Prize worthy: pic.twitter.com/lYogXVP8wj
— Clay Travis (@ClayTravis) March 11, 2025
White House National Security Adviser Michael Waltz said following the talks that "the Ukrainian delegation today made something very clear, that they share President [Donald] Trump's vision for peace, they share his determination to end the fighting, to end the killing, to end the tragic meat grinder of people."
Ukrainian Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha called his country's endorsement of the cease-fire proposal a "step that proves Ukraine is ready to move forward on the path to a just end to the war."
"Ukraine is not an obstacle to peace; it is a partner in its restoration," Sybiha added.
U.S. officials said the cease-fire proposal will now be sent to Russia for approval. It is unclear whether Russian President Vladimir Putin will accept the offer.
"The ball is now in their court," Rubio said of the Russians.
Buoyed by Western support but stretched thin and vastly outmanned and outgunned, Ukrainian forces have been struggling to repel Russia's invasion and hold Russian territory they seized in the Kursk region, with an eye toward potential future territorial exchanges.
On Tuesday, Ukrainian forces launched a massive drone attack on Moscow. Three people were reportedly killed and six others were injured when debris struck a meat processing facility.
Tuesday's development marked a dramatic turnaround from just two weeks ago, when Trump and Vice President JD Vance lambasted Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy during a highly contentious White House meeting that was followed by a suspension of all U.S. military assistance and intelligence-sharing with Kyiv.
The U.S. has "provided $66.5 billion in military assistance since Russia launched its premeditated, unprovoked, and brutal full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, and approximately $69.2 billion in military assistance since Russia's initial invasion of Ukraine in 2014," according to a State Department fact sheet dated March 4.
Keep ReadingShow Less
Watchdog Exposes Millions in Medicare Advantage Lobbying Ahead of Dr. Oz Hearing
"If Oz is confirmed as the CMS administrator, attacks on traditional Medicare are likely to move into overdrive," said one advocate, calling to strengthen the program, "not weaken it through further privatization."
Mar 11, 2025
The watchdog group Public Citizen on Tuesday released a research brief about the hundreds of millions of dollars Medicare Advantage companies have spent on lobbying ahead of a U.S. Senate confirmation hearing for Dr. Mehmet Oz.
Oz, a heart surgeon and former television host, is President Donald Trump's nominee to run the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS)—an agency in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, which is led by conspiracy theorist Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
Health experts and others have sounded the alarm about Oz since Trump announceded his nomination in November, with many opponents highlighting the doctor's investments in companies with direct CMS interests and his push to expand Medicare Advantage when he unsuccessfully ran as a Republican to represent Pennsylvania in the U.S. Senate in 2022.
Medicare Advantage is a type of CMS-approved health insurance plan from a private company that seniors can choose for medical coverage instead of government-administered Medicare. Critics often call it a "profit-seeking healthcare scam."
Public Citizen's brief points out that last year, "more than half of all seniors eligible for Medicare were enrolled" in these private plans that "cost taxpayers hundreds of billions of dollars and deliver inferior care compared to traditional Medicare."
"Since their inception in 2003, Medicare Advantage plans are estimated to have cost taxpayers more than $600 billion in overpayments," the document notes. "These overpayments are expected to grow to $1 trillion over the next decade."
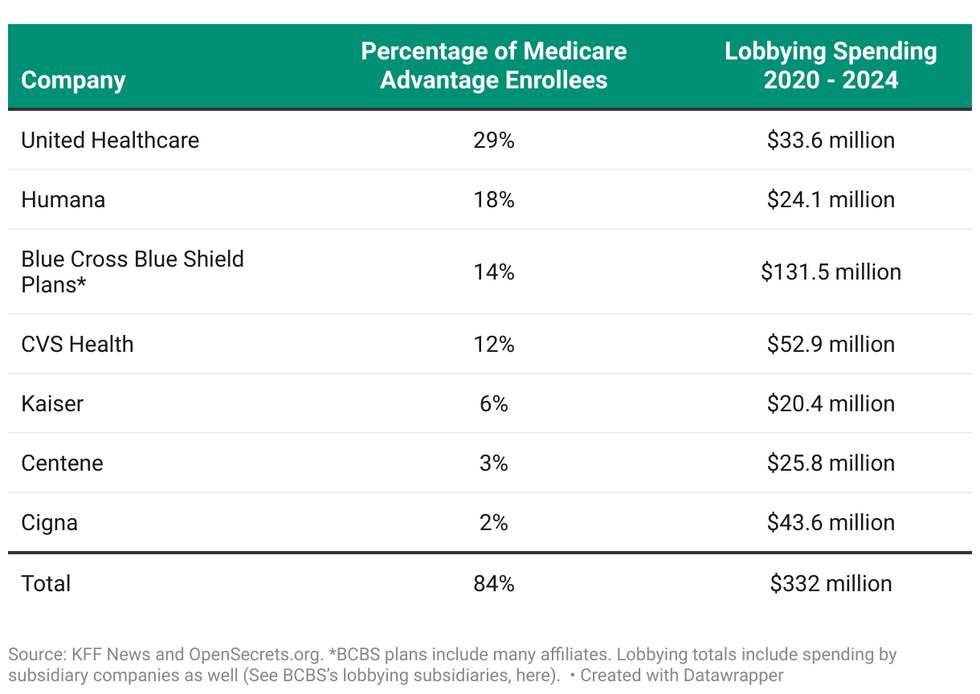
"Just seven companies account for 84% of all Medicare Advantage enrollment," the brief continues. "While lobbying disclosures do not reveal how much is spent on a single issue, disclosures reveal that these seven companies spent more than $330 million combined lobbying on all issues over the last five years, according to data from OpenSecrets."
Those companies are UnitedHealthcare, Humana, Blue Cross Blue Shield, CVS Health, Kaiser, Centene, and Cigna.
Public Citizen found that in 2024, they collectively had 328 lobbyists targeting the federal government, with nearly 70% of them specifically working on Medicare Advantage. Blue Cross had the most lobbyists focused on such plans (99), followed by Humana (33) and UnitedHealth Group (27).
"If Oz is confirmed as the CMS administrator, attacks on traditional Medicare are likely to move into overdrive," Eagan Kemp, a healthcare policy advocate at Public Citizen, warned in a Tuesday statement. "We should strengthen Medicare by improving it and expanding access to it, not weaken it through further privatization."
The Senate Committee on Finance is set to consider Oz on Friday morning. Since Trump returned to the White House in January, the GOP-controlled chamber hasn't blocked any of his nominees.
Keep ReadingShow Less
Most Popular