

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.

Bonnie Miller, 49, left, of Schuylkill, and her daughter, Alyssa, 22, eat hamburgers before the Dine and Dash during the Hamburger Festival in downtown Hamburg, Pennsylvania.
For agriculture as with energy, the real climate solutions are being silenced by the corporate cacophony.
I remember being filled with excitement when the Paris agreement to limit global warming to 1.5°C was adopted by nearly 200 countries at COP21. But after the curtains closed on COP29 last month—almost a decade later—my disenchantment with the event reached a new high.
As early as the 2010s, scientists from academia and the United Nations Environment Program warned that the U.S. and Europe must cut meat consumption by 50% to avoid climate disaster. Earlier COPs had mainly focused on fossil fuels, but meat and dairy corporations undoubtedly saw the writing on the wall that they too would soon come under fire.
Our food system needs to be sustainable for all—people, animals, and our planet.
Animal agriculture accounts for at least 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, over quadruple the amount from global aviation. Global meat and dairy production have increased almost fivefold since the 1960s with the advent of industrialized agriculture. These factory-like systems are characterized by cramming thousands of animals into buildings or feedlots and feeding them unnatural grain diets from crops grown offsite. Even if all fossil fuel use was halted immediately, we would still exceed 1.5°C temperature rise without changing our food system, particularly our production and consumption of animal-sourced foods.
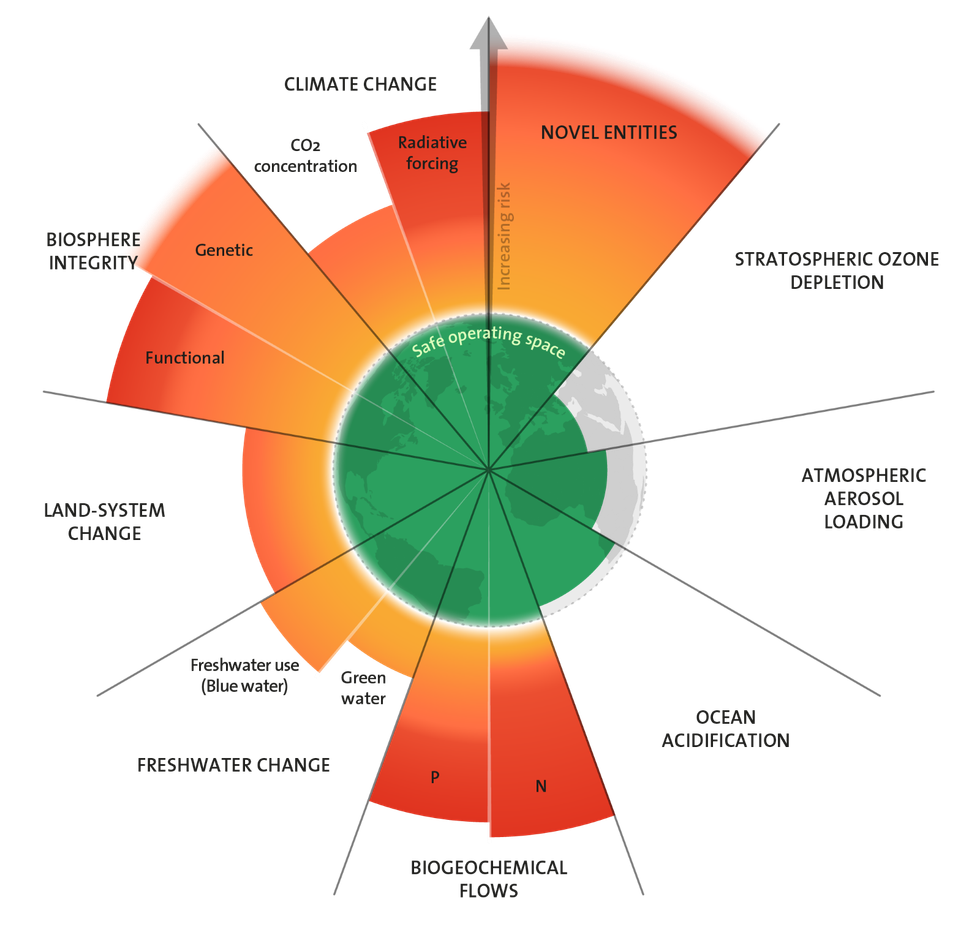
But climate change is just one of the threats we face. We have also breached five other planetary boundaries—biodiversity; land-use change; phosphorus and nitrogen cycling; freshwater use; and pollution from man-made substances such as plastics, antibiotics, and pesticides—all of which are also driven mainly by animal-sourced food production.
By the time world leaders were ready to consider our food system's impact on climate and the environment, the industrialized meat and dairy sector had already prepared its playbook to maintain the status quo. The Conference of Parties is meant to bring together the world's nations and thought leaders to address climate change. However, the event has become increasingly infiltrated by corporate interests. There were 52 delegates from the meat and dairy sector at COP29, many with country badges that gave them privileged access to diplomatic negotiations.
In this forum and others, the industry has peddled bombastic "solutions" under the guise of technology and innovation. Corporate-backed university research has lauded adding seaweed to cattle feed and turning manure lagoons the size of football fields into energy sources to reduce methane production. In Asia, companies are putting pigs in buildings over 20 stories tall, claiming the skyscrapers cut down on space and disease risks. And more recently, Bill Gates and Jeff Bezos started bankrolling research and development into vaccines that reduce the methane-causing bacteria found naturally in cows' stomachs. The industry hopes that the novelty and allure of new technologies will woo lawmakers and investors, but these "solutions" create more problems than they solve, exacerbating net greenhouse gas emissions, air and water pollution, wildlife loss, and freshwater depletion.
Emissions from animal-sourced foods can be broadly divided into four categories: ruminant fermentation (cow burps); manure; logistics (transport, packaging, processing, etc.); and land-use change, i.e., the conversion of wild spaces into pasture, feedlots, and cropland for feed. In the U.S., ruminant fermentation and manure emit more methane than natural gas and petroleum systems combined.
A new report found that beef consumption must decline by over a quarter globally by 2035 to curb methane emissions from cattle, which the industry's solutions claim to solve without needing to reduce consumption. But the direct emissions from cattle aren't the only problem—beef and dairy production is also the leading driver of deforestation, which must decline by 72% by 2035, and reforestation must rise by 115%. About 35% of habitable land is used to raise animals for food or to grow their feed (mostly corn and soy), about the size of North and South America combined.
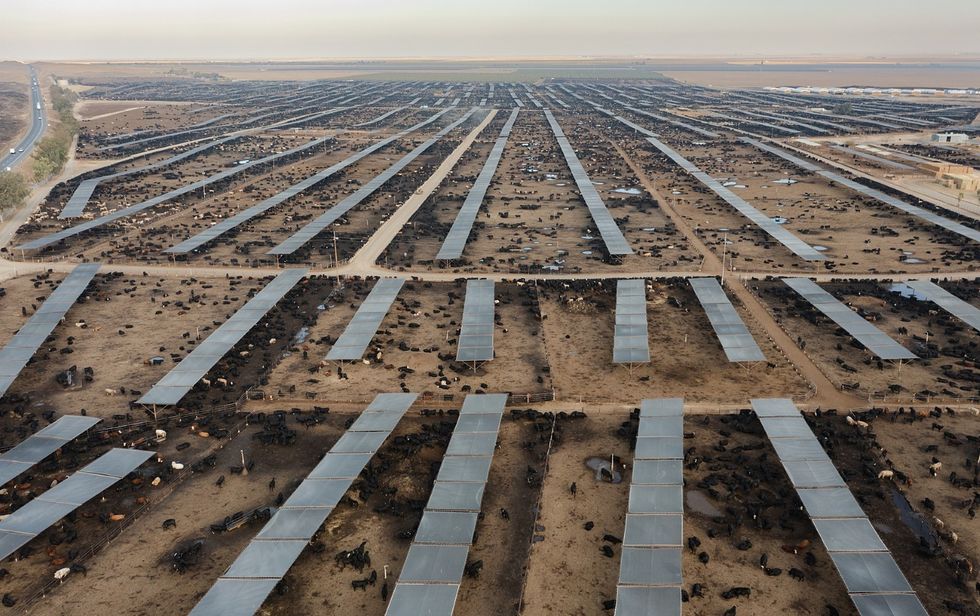

Put simply, the inadequate solutions put forth by Big Ag cannot outpace industrialized farming's negative impacts on the planet. While seaweed and methane vaccines may address cow burps, they don't address carbon emissions from deforestation or manure emissions of nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas over 270 times more powerful than CO2. They also don't address the nitrate water pollution from manure, which can sicken people and cause massive fish kills and harmful algal blooms; biodiversity decline from habitat loss, which has dropped 73% since the rise of industrialized animal agriculture; freshwater use, drying up rivers and accounting for over a quarter of humanity's water footprint; or pesticide use on corn and soy feed, which kills soil microorganisms that are vital to life on Earth.
Skyscrapers, while solving some land-use change, do not consider the resources and the land used to grow animal feed, which is globally about equivalent to the size of Europe. They also don't address the inherent inefficiencies with feeding grain to animals raised for food. If fed directly to people, those grains could feed almost half the world's population. And while the companies using pig skyscrapers claim they enhance biosecurity by keeping potential viruses locked inside, a system failure could spell disaster, posing a bigger threat to wildlife and even humans.
We need both a monumental shift from industrialized agriculture to regenerative systems and a dramatic shift from animal-heavy diets to diets rich in legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, with meat and dairy as a specialty rather than a staple.
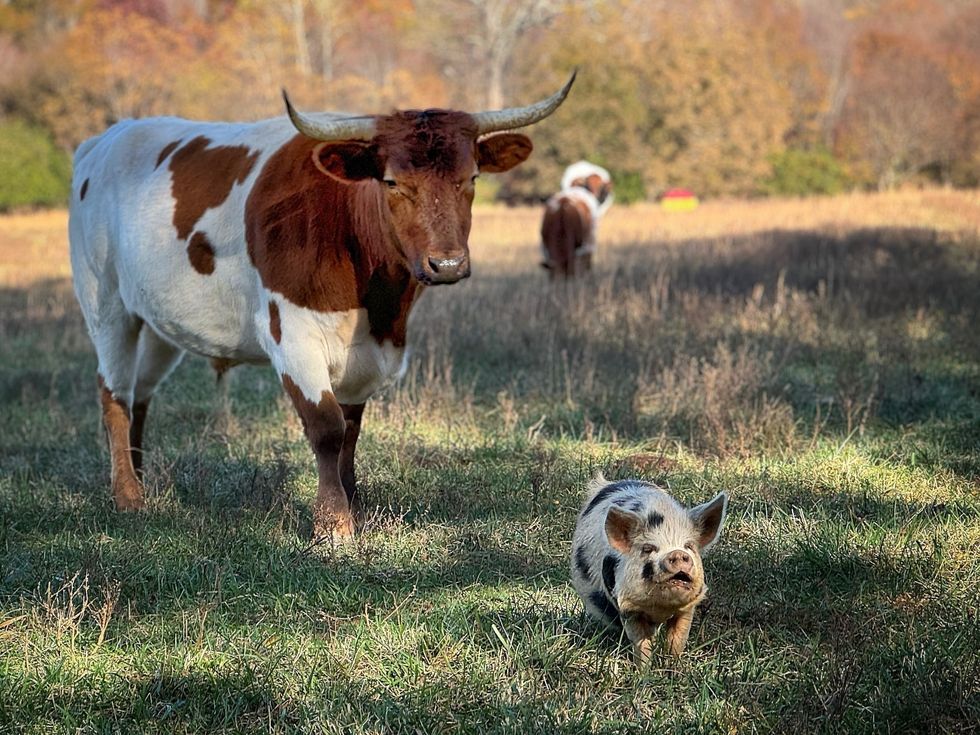
One solution that is gaining traction as an alternative to Big Ag's proposals is regenerative grazing. When done right, regenerative grazing eliminates the need for pesticides and leans into the natural local ecology, putting farm animals onto rotated pastures and facilitating carbon uptake into the soil. Regenerative animal agriculture is arguably the only solution put forward that addresses all six breached planetary boundaries as well as animal welfare and disease risk, and studies suggest it can improve the nutritional quality of animal-sourced foods. While it is imperative to transition from industrialized to regenerative systems, regenerative grazing comes with major caveats. This type of farming is only beneficial in small doses—cutting down centuries-old forests or filling in carbon-rich wetlands to make way for regenerative pastures would do much more climate and ecological harm than good. Soil carbon sequestration takes time and increases with vegetation and undisturbed soil, meaning that any regenerative pastures made today will never be able to capture as much carbon as the original natural landscape, especially in forests, mangroves, wetlands, and tundra. And while regenerative farmlands create better wildlife habitats than feedlots and monocultures, they still don't function like a fully natural ecosystem and food web. Also, cattle emit more methane than their native ruminant counterparts such as bison and deer.
Most notably, however, we simply don't have enough land to produce regeneratively raised animal products at the current consumption rate. Regenerative grazing requires more land than industrialized systems, sometimes two to three times more, and as mentioned the livestock industry already occupies over one-third of the world's habitable land. In all, we have much more to gain from rewilding crop- and rangeland than from turning the world into one big regenerative pasture.

All this brings us to one conclusion—the one that was made by scientists over a decade ago: We need to eat less meat. As Action Aid's Teresa Anderson noted at this year's COP, "The real answers to the climate crisis aren’t being heard over the corporate cacophony."
Scientific climate analyses over the last few years have been grim at best, and apocalyptic at worst. According to one of the latest U.N. reports, limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C (2.7°F) requires cutting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 57% by 2035, relative to 2023 emissions. However, current national policies—none of which currently include diet shifts—will achieve less than a 1% reduction by 2035. If the 54 wealthiest nations adopted sustainable healthy diets with modest amounts of animal products, they could slash their total emissions by 61%. If we also allowed the leftover land to rewild, we could sequester 30% of our global carbon budget in these nations and nearly 100% if adopted globally.
Our food system needs to be sustainable for all—people, animals, and our planet. Quick fixes and bandages will not save our planet from climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution. We need both a monumental shift from industrialized agriculture to regenerative systems and a dramatic shift from animal-heavy diets to diets rich in legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, with meat and dairy as a specialty rather than a staple. As nations draft their policies for COP30, due early this year, we need leaders to adopt real food system solutions instead of buying into the corporate cacophony.
Trump and Musk are on an unconstitutional rampage, aiming for virtually every corner of the federal government. These two right-wing billionaires are targeting nurses, scientists, teachers, daycare providers, judges, veterans, air traffic controllers, and nuclear safety inspectors. No one is safe. The food stamps program, Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid are next. It’s an unprecedented disaster and a five-alarm fire, but there will be a reckoning. The people did not vote for this. The American people do not want this dystopian hellscape that hides behind claims of “efficiency.” Still, in reality, it is all a giveaway to corporate interests and the libertarian dreams of far-right oligarchs like Musk. Common Dreams is playing a vital role by reporting day and night on this orgy of corruption and greed, as well as what everyday people can do to organize and fight back. As a people-powered nonprofit news outlet, we cover issues the corporate media never will, but we can only continue with our readers’ support. |
I remember being filled with excitement when the Paris agreement to limit global warming to 1.5°C was adopted by nearly 200 countries at COP21. But after the curtains closed on COP29 last month—almost a decade later—my disenchantment with the event reached a new high.
As early as the 2010s, scientists from academia and the United Nations Environment Program warned that the U.S. and Europe must cut meat consumption by 50% to avoid climate disaster. Earlier COPs had mainly focused on fossil fuels, but meat and dairy corporations undoubtedly saw the writing on the wall that they too would soon come under fire.
Our food system needs to be sustainable for all—people, animals, and our planet.
Animal agriculture accounts for at least 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, over quadruple the amount from global aviation. Global meat and dairy production have increased almost fivefold since the 1960s with the advent of industrialized agriculture. These factory-like systems are characterized by cramming thousands of animals into buildings or feedlots and feeding them unnatural grain diets from crops grown offsite. Even if all fossil fuel use was halted immediately, we would still exceed 1.5°C temperature rise without changing our food system, particularly our production and consumption of animal-sourced foods.
But climate change is just one of the threats we face. We have also breached five other planetary boundaries—biodiversity; land-use change; phosphorus and nitrogen cycling; freshwater use; and pollution from man-made substances such as plastics, antibiotics, and pesticides—all of which are also driven mainly by animal-sourced food production.

By the time world leaders were ready to consider our food system's impact on climate and the environment, the industrialized meat and dairy sector had already prepared its playbook to maintain the status quo. The Conference of Parties is meant to bring together the world's nations and thought leaders to address climate change. However, the event has become increasingly infiltrated by corporate interests. There were 52 delegates from the meat and dairy sector at COP29, many with country badges that gave them privileged access to diplomatic negotiations.
In this forum and others, the industry has peddled bombastic "solutions" under the guise of technology and innovation. Corporate-backed university research has lauded adding seaweed to cattle feed and turning manure lagoons the size of football fields into energy sources to reduce methane production. In Asia, companies are putting pigs in buildings over 20 stories tall, claiming the skyscrapers cut down on space and disease risks. And more recently, Bill Gates and Jeff Bezos started bankrolling research and development into vaccines that reduce the methane-causing bacteria found naturally in cows' stomachs. The industry hopes that the novelty and allure of new technologies will woo lawmakers and investors, but these "solutions" create more problems than they solve, exacerbating net greenhouse gas emissions, air and water pollution, wildlife loss, and freshwater depletion.
Emissions from animal-sourced foods can be broadly divided into four categories: ruminant fermentation (cow burps); manure; logistics (transport, packaging, processing, etc.); and land-use change, i.e., the conversion of wild spaces into pasture, feedlots, and cropland for feed. In the U.S., ruminant fermentation and manure emit more methane than natural gas and petroleum systems combined.
A new report found that beef consumption must decline by over a quarter globally by 2035 to curb methane emissions from cattle, which the industry's solutions claim to solve without needing to reduce consumption. But the direct emissions from cattle aren't the only problem—beef and dairy production is also the leading driver of deforestation, which must decline by 72% by 2035, and reforestation must rise by 115%. About 35% of habitable land is used to raise animals for food or to grow their feed (mostly corn and soy), about the size of North and South America combined.

Put simply, the inadequate solutions put forth by Big Ag cannot outpace industrialized farming's negative impacts on the planet. While seaweed and methane vaccines may address cow burps, they don't address carbon emissions from deforestation or manure emissions of nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas over 270 times more powerful than CO2. They also don't address the nitrate water pollution from manure, which can sicken people and cause massive fish kills and harmful algal blooms; biodiversity decline from habitat loss, which has dropped 73% since the rise of industrialized animal agriculture; freshwater use, drying up rivers and accounting for over a quarter of humanity's water footprint; or pesticide use on corn and soy feed, which kills soil microorganisms that are vital to life on Earth.
Skyscrapers, while solving some land-use change, do not consider the resources and the land used to grow animal feed, which is globally about equivalent to the size of Europe. They also don't address the inherent inefficiencies with feeding grain to animals raised for food. If fed directly to people, those grains could feed almost half the world's population. And while the companies using pig skyscrapers claim they enhance biosecurity by keeping potential viruses locked inside, a system failure could spell disaster, posing a bigger threat to wildlife and even humans.
We need both a monumental shift from industrialized agriculture to regenerative systems and a dramatic shift from animal-heavy diets to diets rich in legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, with meat and dairy as a specialty rather than a staple.
One solution that is gaining traction as an alternative to Big Ag's proposals is regenerative grazing. When done right, regenerative grazing eliminates the need for pesticides and leans into the natural local ecology, putting farm animals onto rotated pastures and facilitating carbon uptake into the soil. Regenerative animal agriculture is arguably the only solution put forward that addresses all six breached planetary boundaries as well as animal welfare and disease risk, and studies suggest it can improve the nutritional quality of animal-sourced foods. While it is imperative to transition from industrialized to regenerative systems, regenerative grazing comes with major caveats. This type of farming is only beneficial in small doses—cutting down centuries-old forests or filling in carbon-rich wetlands to make way for regenerative pastures would do much more climate and ecological harm than good. Soil carbon sequestration takes time and increases with vegetation and undisturbed soil, meaning that any regenerative pastures made today will never be able to capture as much carbon as the original natural landscape, especially in forests, mangroves, wetlands, and tundra. And while regenerative farmlands create better wildlife habitats than feedlots and monocultures, they still don't function like a fully natural ecosystem and food web. Also, cattle emit more methane than their native ruminant counterparts such as bison and deer.
Most notably, however, we simply don't have enough land to produce regeneratively raised animal products at the current consumption rate. Regenerative grazing requires more land than industrialized systems, sometimes two to three times more, and as mentioned the livestock industry already occupies over one-third of the world's habitable land. In all, we have much more to gain from rewilding crop- and rangeland than from turning the world into one big regenerative pasture.

All this brings us to one conclusion—the one that was made by scientists over a decade ago: We need to eat less meat. As Action Aid's Teresa Anderson noted at this year's COP, "The real answers to the climate crisis aren’t being heard over the corporate cacophony."
Scientific climate analyses over the last few years have been grim at best, and apocalyptic at worst. According to one of the latest U.N. reports, limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C (2.7°F) requires cutting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 57% by 2035, relative to 2023 emissions. However, current national policies—none of which currently include diet shifts—will achieve less than a 1% reduction by 2035. If the 54 wealthiest nations adopted sustainable healthy diets with modest amounts of animal products, they could slash their total emissions by 61%. If we also allowed the leftover land to rewild, we could sequester 30% of our global carbon budget in these nations and nearly 100% if adopted globally.
Our food system needs to be sustainable for all—people, animals, and our planet. Quick fixes and bandages will not save our planet from climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution. We need both a monumental shift from industrialized agriculture to regenerative systems and a dramatic shift from animal-heavy diets to diets rich in legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, with meat and dairy as a specialty rather than a staple. As nations draft their policies for COP30, due early this year, we need leaders to adopt real food system solutions instead of buying into the corporate cacophony.
I remember being filled with excitement when the Paris agreement to limit global warming to 1.5°C was adopted by nearly 200 countries at COP21. But after the curtains closed on COP29 last month—almost a decade later—my disenchantment with the event reached a new high.
As early as the 2010s, scientists from academia and the United Nations Environment Program warned that the U.S. and Europe must cut meat consumption by 50% to avoid climate disaster. Earlier COPs had mainly focused on fossil fuels, but meat and dairy corporations undoubtedly saw the writing on the wall that they too would soon come under fire.
Our food system needs to be sustainable for all—people, animals, and our planet.
Animal agriculture accounts for at least 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, over quadruple the amount from global aviation. Global meat and dairy production have increased almost fivefold since the 1960s with the advent of industrialized agriculture. These factory-like systems are characterized by cramming thousands of animals into buildings or feedlots and feeding them unnatural grain diets from crops grown offsite. Even if all fossil fuel use was halted immediately, we would still exceed 1.5°C temperature rise without changing our food system, particularly our production and consumption of animal-sourced foods.
But climate change is just one of the threats we face. We have also breached five other planetary boundaries—biodiversity; land-use change; phosphorus and nitrogen cycling; freshwater use; and pollution from man-made substances such as plastics, antibiotics, and pesticides—all of which are also driven mainly by animal-sourced food production.

By the time world leaders were ready to consider our food system's impact on climate and the environment, the industrialized meat and dairy sector had already prepared its playbook to maintain the status quo. The Conference of Parties is meant to bring together the world's nations and thought leaders to address climate change. However, the event has become increasingly infiltrated by corporate interests. There were 52 delegates from the meat and dairy sector at COP29, many with country badges that gave them privileged access to diplomatic negotiations.
In this forum and others, the industry has peddled bombastic "solutions" under the guise of technology and innovation. Corporate-backed university research has lauded adding seaweed to cattle feed and turning manure lagoons the size of football fields into energy sources to reduce methane production. In Asia, companies are putting pigs in buildings over 20 stories tall, claiming the skyscrapers cut down on space and disease risks. And more recently, Bill Gates and Jeff Bezos started bankrolling research and development into vaccines that reduce the methane-causing bacteria found naturally in cows' stomachs. The industry hopes that the novelty and allure of new technologies will woo lawmakers and investors, but these "solutions" create more problems than they solve, exacerbating net greenhouse gas emissions, air and water pollution, wildlife loss, and freshwater depletion.
Emissions from animal-sourced foods can be broadly divided into four categories: ruminant fermentation (cow burps); manure; logistics (transport, packaging, processing, etc.); and land-use change, i.e., the conversion of wild spaces into pasture, feedlots, and cropland for feed. In the U.S., ruminant fermentation and manure emit more methane than natural gas and petroleum systems combined.
A new report found that beef consumption must decline by over a quarter globally by 2035 to curb methane emissions from cattle, which the industry's solutions claim to solve without needing to reduce consumption. But the direct emissions from cattle aren't the only problem—beef and dairy production is also the leading driver of deforestation, which must decline by 72% by 2035, and reforestation must rise by 115%. About 35% of habitable land is used to raise animals for food or to grow their feed (mostly corn and soy), about the size of North and South America combined.

Put simply, the inadequate solutions put forth by Big Ag cannot outpace industrialized farming's negative impacts on the planet. While seaweed and methane vaccines may address cow burps, they don't address carbon emissions from deforestation or manure emissions of nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas over 270 times more powerful than CO2. They also don't address the nitrate water pollution from manure, which can sicken people and cause massive fish kills and harmful algal blooms; biodiversity decline from habitat loss, which has dropped 73% since the rise of industrialized animal agriculture; freshwater use, drying up rivers and accounting for over a quarter of humanity's water footprint; or pesticide use on corn and soy feed, which kills soil microorganisms that are vital to life on Earth.
Skyscrapers, while solving some land-use change, do not consider the resources and the land used to grow animal feed, which is globally about equivalent to the size of Europe. They also don't address the inherent inefficiencies with feeding grain to animals raised for food. If fed directly to people, those grains could feed almost half the world's population. And while the companies using pig skyscrapers claim they enhance biosecurity by keeping potential viruses locked inside, a system failure could spell disaster, posing a bigger threat to wildlife and even humans.
We need both a monumental shift from industrialized agriculture to regenerative systems and a dramatic shift from animal-heavy diets to diets rich in legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, with meat and dairy as a specialty rather than a staple.
One solution that is gaining traction as an alternative to Big Ag's proposals is regenerative grazing. When done right, regenerative grazing eliminates the need for pesticides and leans into the natural local ecology, putting farm animals onto rotated pastures and facilitating carbon uptake into the soil. Regenerative animal agriculture is arguably the only solution put forward that addresses all six breached planetary boundaries as well as animal welfare and disease risk, and studies suggest it can improve the nutritional quality of animal-sourced foods. While it is imperative to transition from industrialized to regenerative systems, regenerative grazing comes with major caveats. This type of farming is only beneficial in small doses—cutting down centuries-old forests or filling in carbon-rich wetlands to make way for regenerative pastures would do much more climate and ecological harm than good. Soil carbon sequestration takes time and increases with vegetation and undisturbed soil, meaning that any regenerative pastures made today will never be able to capture as much carbon as the original natural landscape, especially in forests, mangroves, wetlands, and tundra. And while regenerative farmlands create better wildlife habitats than feedlots and monocultures, they still don't function like a fully natural ecosystem and food web. Also, cattle emit more methane than their native ruminant counterparts such as bison and deer.
Most notably, however, we simply don't have enough land to produce regeneratively raised animal products at the current consumption rate. Regenerative grazing requires more land than industrialized systems, sometimes two to three times more, and as mentioned the livestock industry already occupies over one-third of the world's habitable land. In all, we have much more to gain from rewilding crop- and rangeland than from turning the world into one big regenerative pasture.

All this brings us to one conclusion—the one that was made by scientists over a decade ago: We need to eat less meat. As Action Aid's Teresa Anderson noted at this year's COP, "The real answers to the climate crisis aren’t being heard over the corporate cacophony."
Scientific climate analyses over the last few years have been grim at best, and apocalyptic at worst. According to one of the latest U.N. reports, limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C (2.7°F) requires cutting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 57% by 2035, relative to 2023 emissions. However, current national policies—none of which currently include diet shifts—will achieve less than a 1% reduction by 2035. If the 54 wealthiest nations adopted sustainable healthy diets with modest amounts of animal products, they could slash their total emissions by 61%. If we also allowed the leftover land to rewild, we could sequester 30% of our global carbon budget in these nations and nearly 100% if adopted globally.
Our food system needs to be sustainable for all—people, animals, and our planet. Quick fixes and bandages will not save our planet from climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution. We need both a monumental shift from industrialized agriculture to regenerative systems and a dramatic shift from animal-heavy diets to diets rich in legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, with meat and dairy as a specialty rather than a staple. As nations draft their policies for COP30, due early this year, we need leaders to adopt real food system solutions instead of buying into the corporate cacophony.