

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
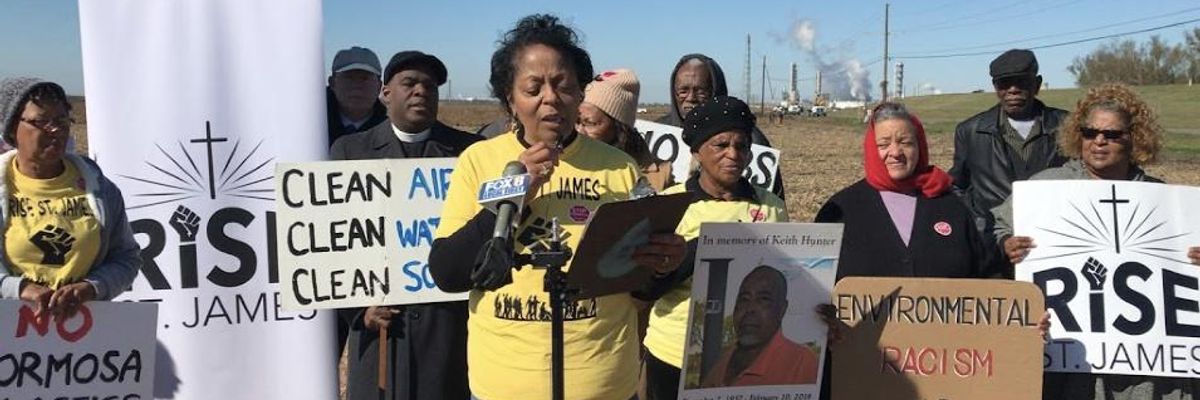

Local activists are organizing to block a petrochemical complex from being in St. James Parish, Louisiana, citing pollution concerns and a discovery that the site served as burial grounds for enslaved people.
Policymakers, investors, and communities must confront the reality that the continued expansion of petrochemical infrastructure is incompatible with a sustainable future.
The U.S. is on the brink of making a major climate misstep.
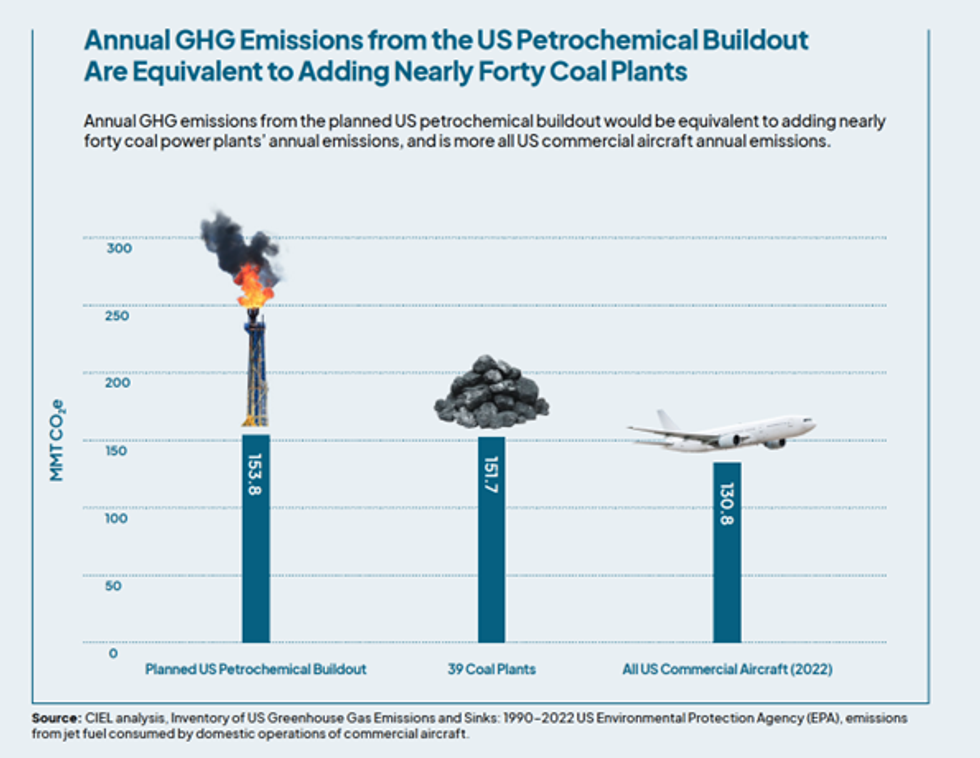
According to a new Center for International Environmental Law analysis, planned petrochemical projects across the U.S. could add a staggering 153.8 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO₂e) emissions annually. This is equal to the emissions of nearly 40 coal power plants or all U.S. domestic commercial aviation emissions. The implications for climate change are dire, with the petrochemical sector set to become an even larger contributor to the country’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
In a time when decisive climate action is needed more than ever, building more petrochemical plants is a monumental mistake the U.S. cannot afford to make.
Already responsible for 5.2% of the U.S.’ 6.3 billion metric tonnes of annual CO₂e emissions, the petrochemical industry is poised for massive growth. A total of 118 petrochemical projects—ranging from the expansion of existing plants to the construction of entirely new plants—are either planned or already underway and could add the equivalent of 2.4% of all U.S. greenhouse gas emissions. If this buildout proceeds, more than 7% of U.S. GHG emissions could come from the petrochemical sector.

Petrochemical plants manufacture products like plastics, ammonia, and other chemicals, and have a typical lifespan of about 30 years. This means that the fossil-fueled emissions from these facilities will persist for decades, hindering the U.S.’ ability to meet its climate targets. Globally, the petrochemical sector is already a major climate problem, responsible for around 10% of total GHG emissions. Plastic production alone contributes 5.3% of global emissions, while synthetic nitrogen fertilizers add another 2.1% of global emissions.
In a recent analysis, the International Energy Agency projected that 85% of the growth in oil demand will come from petrochemical production by 2030. In the U.S., the planned petrochemical buildout will only make this worse. Our analysis not only reaffirms what we already know about the petrochemical industry’s impact but also highlights new and concerning developments.
The environmental impact of the petrochemical buildout extends far beyond its contribution to climate change. The petrochemical buildout will deepen environmental injustices in communities that already bear the brunt of industrial pollution. The vast majority of planned petrochemical projects are sited in communities that already experience detrimental environmental and health impacts of living on the fence line of the fossil fuel industry, particularly in the Gulf South and Ohio River Valley.
In Louisiana’s “Cancer Alley,” a region between New Orleans and Baton Rouge, 26 new petrochemical projects are planned. This area is already home to more than 200 fossil fuel and chemical facilities where residents face some of the highest cancer rates in the country. In St. John the Baptist Parish, around halfway between the two cities, lifetime cancer rates are 800 times the U.S. average, according to an estimate from the Environmental Protection Agency. The expansion of petrochemical plants in these communities will only deepen the public health crisis.
Megaprojects Make Up Most of the Emissions
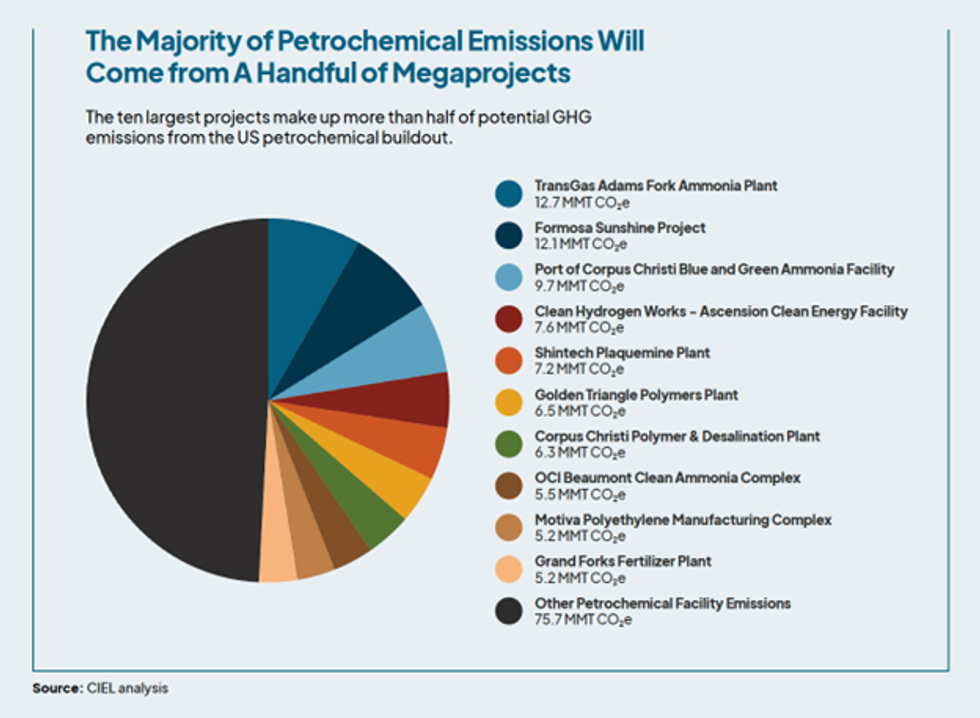
One of the most alarming revelations from our analysis is that just 10 megaprojects account for half of the potential emissions from the petrochemical buildout. The fate of just a handful of projects will have a massive impact on the U.S.’ ability to meet its climate targets.
Plastic Production Is Facing Serious Roadblocks
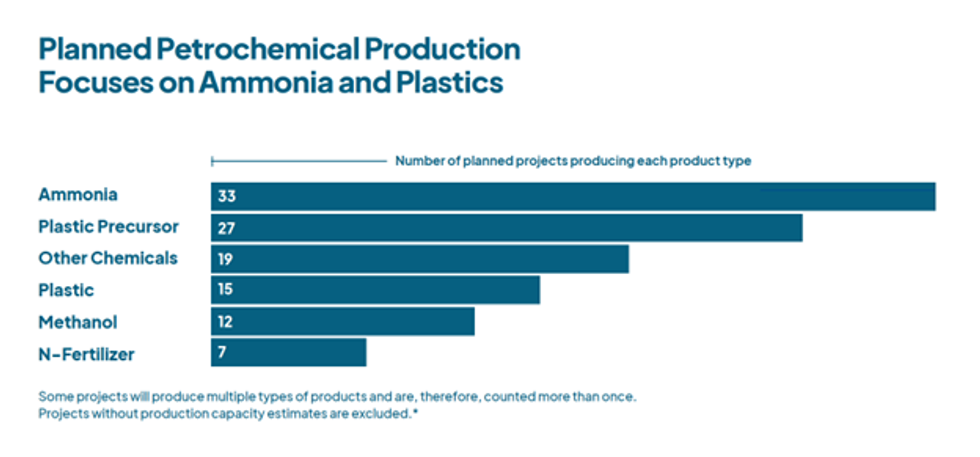
Nearly 60% of planned plastic production projects, calculated based on potential emissions, are on hold. This suggests that investors are already assessing significant risks around the future of plastic production. The growing awareness of the environmental damage caused by plastics, community opposition to these plants, and a global overcapacity of plastic production may be giving investors pause.
Ammonia, A Huge Growth Sector
Ammonia, primarily used in fertilizers, is emerging as a concerning climate problem. More than a third of the projected new emissions come from planned ammonia production. Companies behind projected projects are pitching ammonia not just for fertilizers but as a clean “fuel of the future.” findings reveal that these projects are anything but “clean,” with 95% of proposed U.S. ammonia production being derived from methane gas, which undercuts its supposed climate benefit.
Taxpayers are Footing the Bill
Adding insult to injury, many of these projects are being subsidized by U.S. taxpayers. Planned ammonia and methanol plants stand to benefit from U.S. government incentives like 45Q tax credits, which provide generous handouts to companies using carbon capture systems (CCS) despite carbon capture’s long record of failure.
To work out emissions from these planned petrochemical projects we dug through companies’ websites, press releases, and investor communications as well as consulted the Environmental Integrity Project’s comprehensive Oil and Gas Watch database to find the potential production capacity of new petrochemical projects. We used “emissions factors” published by academics at the Universities of Cambridge, Bath, and Sheffield to turn those production numbers into an estimate of emissions, and incorporated the expected emissions from fertilizer decomposition and plastic incineration.
Despite our careful math, we know our calculations underestimate the true climate harm these projects could bring. A few factors contribute to our conservative figures. First, we were only able to estimate emissions from two-thirds of the potential projects. Second, the models we use rely on the U.S. Department of Energy’s estimate of methane leakage, but recent studies suggest that methane leaks are three times higher than this figure. Finally, we cannot quantify some of the potential impacts that plastic pollution or overuse of fertilizers might be having, but there are worrying studies suggesting that both could have deep climate impacts.
Having just experienced the warmest summer on record, the need to phase out fossil fuels has never been more clear. The US petrochemical buildout is a leap in the wrong direction—one that will lock in fossil fuel demand at a time when we should be transitioning away from them.
The decisions made about these projects will have far-reaching consequences. Our analysis reveals the high stakes and urgent need to question whether these projects should be allowed to move forward.
The U.S. is at a crossroads. Policymakers, investors, and communities must confront the reality that the continued expansion of petrochemical infrastructure is incompatible with a sustainable future. The fate of these projects will not only shape the U.S.’ climate trajectory but also have global repercussions in the fight to curb fossil fuel emissions and protect communities vulnerable to the compounding impacts of the petrochemical buildout.
In a time when decisive climate action is needed more than ever, building more petrochemical plants is a monumental mistake the U.S. cannot afford to make. The time to act is now.
Trump and Musk are on an unconstitutional rampage, aiming for virtually every corner of the federal government. These two right-wing billionaires are targeting nurses, scientists, teachers, daycare providers, judges, veterans, air traffic controllers, and nuclear safety inspectors. No one is safe. The food stamps program, Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid are next. It’s an unprecedented disaster and a five-alarm fire, but there will be a reckoning. The people did not vote for this. The American people do not want this dystopian hellscape that hides behind claims of “efficiency.” Still, in reality, it is all a giveaway to corporate interests and the libertarian dreams of far-right oligarchs like Musk. Common Dreams is playing a vital role by reporting day and night on this orgy of corruption and greed, as well as what everyday people can do to organize and fight back. As a people-powered nonprofit news outlet, we cover issues the corporate media never will, but we can only continue with our readers’ support. |
The U.S. is on the brink of making a major climate misstep.
According to a new Center for International Environmental Law analysis, planned petrochemical projects across the U.S. could add a staggering 153.8 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO₂e) emissions annually. This is equal to the emissions of nearly 40 coal power plants or all U.S. domestic commercial aviation emissions. The implications for climate change are dire, with the petrochemical sector set to become an even larger contributor to the country’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
In a time when decisive climate action is needed more than ever, building more petrochemical plants is a monumental mistake the U.S. cannot afford to make.
Already responsible for 5.2% of the U.S.’ 6.3 billion metric tonnes of annual CO₂e emissions, the petrochemical industry is poised for massive growth. A total of 118 petrochemical projects—ranging from the expansion of existing plants to the construction of entirely new plants—are either planned or already underway and could add the equivalent of 2.4% of all U.S. greenhouse gas emissions. If this buildout proceeds, more than 7% of U.S. GHG emissions could come from the petrochemical sector.


Petrochemical plants manufacture products like plastics, ammonia, and other chemicals, and have a typical lifespan of about 30 years. This means that the fossil-fueled emissions from these facilities will persist for decades, hindering the U.S.’ ability to meet its climate targets. Globally, the petrochemical sector is already a major climate problem, responsible for around 10% of total GHG emissions. Plastic production alone contributes 5.3% of global emissions, while synthetic nitrogen fertilizers add another 2.1% of global emissions.
In a recent analysis, the International Energy Agency projected that 85% of the growth in oil demand will come from petrochemical production by 2030. In the U.S., the planned petrochemical buildout will only make this worse. Our analysis not only reaffirms what we already know about the petrochemical industry’s impact but also highlights new and concerning developments.
The environmental impact of the petrochemical buildout extends far beyond its contribution to climate change. The petrochemical buildout will deepen environmental injustices in communities that already bear the brunt of industrial pollution. The vast majority of planned petrochemical projects are sited in communities that already experience detrimental environmental and health impacts of living on the fence line of the fossil fuel industry, particularly in the Gulf South and Ohio River Valley.
In Louisiana’s “Cancer Alley,” a region between New Orleans and Baton Rouge, 26 new petrochemical projects are planned. This area is already home to more than 200 fossil fuel and chemical facilities where residents face some of the highest cancer rates in the country. In St. John the Baptist Parish, around halfway between the two cities, lifetime cancer rates are 800 times the U.S. average, according to an estimate from the Environmental Protection Agency. The expansion of petrochemical plants in these communities will only deepen the public health crisis.

Megaprojects Make Up Most of the Emissions
One of the most alarming revelations from our analysis is that just 10 megaprojects account for half of the potential emissions from the petrochemical buildout. The fate of just a handful of projects will have a massive impact on the U.S.’ ability to meet its climate targets.
Plastic Production Is Facing Serious Roadblocks
Nearly 60% of planned plastic production projects, calculated based on potential emissions, are on hold. This suggests that investors are already assessing significant risks around the future of plastic production. The growing awareness of the environmental damage caused by plastics, community opposition to these plants, and a global overcapacity of plastic production may be giving investors pause.
Ammonia, A Huge Growth Sector
Ammonia, primarily used in fertilizers, is emerging as a concerning climate problem. More than a third of the projected new emissions come from planned ammonia production. Companies behind projected projects are pitching ammonia not just for fertilizers but as a clean “fuel of the future.” findings reveal that these projects are anything but “clean,” with 95% of proposed U.S. ammonia production being derived from methane gas, which undercuts its supposed climate benefit.

Taxpayers are Footing the Bill
Adding insult to injury, many of these projects are being subsidized by U.S. taxpayers. Planned ammonia and methanol plants stand to benefit from U.S. government incentives like 45Q tax credits, which provide generous handouts to companies using carbon capture systems (CCS) despite carbon capture’s long record of failure.
To work out emissions from these planned petrochemical projects we dug through companies’ websites, press releases, and investor communications as well as consulted the Environmental Integrity Project’s comprehensive Oil and Gas Watch database to find the potential production capacity of new petrochemical projects. We used “emissions factors” published by academics at the Universities of Cambridge, Bath, and Sheffield to turn those production numbers into an estimate of emissions, and incorporated the expected emissions from fertilizer decomposition and plastic incineration.
Despite our careful math, we know our calculations underestimate the true climate harm these projects could bring. A few factors contribute to our conservative figures. First, we were only able to estimate emissions from two-thirds of the potential projects. Second, the models we use rely on the U.S. Department of Energy’s estimate of methane leakage, but recent studies suggest that methane leaks are three times higher than this figure. Finally, we cannot quantify some of the potential impacts that plastic pollution or overuse of fertilizers might be having, but there are worrying studies suggesting that both could have deep climate impacts.
Having just experienced the warmest summer on record, the need to phase out fossil fuels has never been more clear. The US petrochemical buildout is a leap in the wrong direction—one that will lock in fossil fuel demand at a time when we should be transitioning away from them.
The decisions made about these projects will have far-reaching consequences. Our analysis reveals the high stakes and urgent need to question whether these projects should be allowed to move forward.
The U.S. is at a crossroads. Policymakers, investors, and communities must confront the reality that the continued expansion of petrochemical infrastructure is incompatible with a sustainable future. The fate of these projects will not only shape the U.S.’ climate trajectory but also have global repercussions in the fight to curb fossil fuel emissions and protect communities vulnerable to the compounding impacts of the petrochemical buildout.
In a time when decisive climate action is needed more than ever, building more petrochemical plants is a monumental mistake the U.S. cannot afford to make. The time to act is now.
The U.S. is on the brink of making a major climate misstep.
According to a new Center for International Environmental Law analysis, planned petrochemical projects across the U.S. could add a staggering 153.8 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO₂e) emissions annually. This is equal to the emissions of nearly 40 coal power plants or all U.S. domestic commercial aviation emissions. The implications for climate change are dire, with the petrochemical sector set to become an even larger contributor to the country’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
In a time when decisive climate action is needed more than ever, building more petrochemical plants is a monumental mistake the U.S. cannot afford to make.
Already responsible for 5.2% of the U.S.’ 6.3 billion metric tonnes of annual CO₂e emissions, the petrochemical industry is poised for massive growth. A total of 118 petrochemical projects—ranging from the expansion of existing plants to the construction of entirely new plants—are either planned or already underway and could add the equivalent of 2.4% of all U.S. greenhouse gas emissions. If this buildout proceeds, more than 7% of U.S. GHG emissions could come from the petrochemical sector.


Petrochemical plants manufacture products like plastics, ammonia, and other chemicals, and have a typical lifespan of about 30 years. This means that the fossil-fueled emissions from these facilities will persist for decades, hindering the U.S.’ ability to meet its climate targets. Globally, the petrochemical sector is already a major climate problem, responsible for around 10% of total GHG emissions. Plastic production alone contributes 5.3% of global emissions, while synthetic nitrogen fertilizers add another 2.1% of global emissions.
In a recent analysis, the International Energy Agency projected that 85% of the growth in oil demand will come from petrochemical production by 2030. In the U.S., the planned petrochemical buildout will only make this worse. Our analysis not only reaffirms what we already know about the petrochemical industry’s impact but also highlights new and concerning developments.
The environmental impact of the petrochemical buildout extends far beyond its contribution to climate change. The petrochemical buildout will deepen environmental injustices in communities that already bear the brunt of industrial pollution. The vast majority of planned petrochemical projects are sited in communities that already experience detrimental environmental and health impacts of living on the fence line of the fossil fuel industry, particularly in the Gulf South and Ohio River Valley.
In Louisiana’s “Cancer Alley,” a region between New Orleans and Baton Rouge, 26 new petrochemical projects are planned. This area is already home to more than 200 fossil fuel and chemical facilities where residents face some of the highest cancer rates in the country. In St. John the Baptist Parish, around halfway between the two cities, lifetime cancer rates are 800 times the U.S. average, according to an estimate from the Environmental Protection Agency. The expansion of petrochemical plants in these communities will only deepen the public health crisis.

Megaprojects Make Up Most of the Emissions
One of the most alarming revelations from our analysis is that just 10 megaprojects account for half of the potential emissions from the petrochemical buildout. The fate of just a handful of projects will have a massive impact on the U.S.’ ability to meet its climate targets.
Plastic Production Is Facing Serious Roadblocks
Nearly 60% of planned plastic production projects, calculated based on potential emissions, are on hold. This suggests that investors are already assessing significant risks around the future of plastic production. The growing awareness of the environmental damage caused by plastics, community opposition to these plants, and a global overcapacity of plastic production may be giving investors pause.
Ammonia, A Huge Growth Sector
Ammonia, primarily used in fertilizers, is emerging as a concerning climate problem. More than a third of the projected new emissions come from planned ammonia production. Companies behind projected projects are pitching ammonia not just for fertilizers but as a clean “fuel of the future.” findings reveal that these projects are anything but “clean,” with 95% of proposed U.S. ammonia production being derived from methane gas, which undercuts its supposed climate benefit.

Taxpayers are Footing the Bill
Adding insult to injury, many of these projects are being subsidized by U.S. taxpayers. Planned ammonia and methanol plants stand to benefit from U.S. government incentives like 45Q tax credits, which provide generous handouts to companies using carbon capture systems (CCS) despite carbon capture’s long record of failure.
To work out emissions from these planned petrochemical projects we dug through companies’ websites, press releases, and investor communications as well as consulted the Environmental Integrity Project’s comprehensive Oil and Gas Watch database to find the potential production capacity of new petrochemical projects. We used “emissions factors” published by academics at the Universities of Cambridge, Bath, and Sheffield to turn those production numbers into an estimate of emissions, and incorporated the expected emissions from fertilizer decomposition and plastic incineration.
Despite our careful math, we know our calculations underestimate the true climate harm these projects could bring. A few factors contribute to our conservative figures. First, we were only able to estimate emissions from two-thirds of the potential projects. Second, the models we use rely on the U.S. Department of Energy’s estimate of methane leakage, but recent studies suggest that methane leaks are three times higher than this figure. Finally, we cannot quantify some of the potential impacts that plastic pollution or overuse of fertilizers might be having, but there are worrying studies suggesting that both could have deep climate impacts.
Having just experienced the warmest summer on record, the need to phase out fossil fuels has never been more clear. The US petrochemical buildout is a leap in the wrong direction—one that will lock in fossil fuel demand at a time when we should be transitioning away from them.
The decisions made about these projects will have far-reaching consequences. Our analysis reveals the high stakes and urgent need to question whether these projects should be allowed to move forward.
The U.S. is at a crossroads. Policymakers, investors, and communities must confront the reality that the continued expansion of petrochemical infrastructure is incompatible with a sustainable future. The fate of these projects will not only shape the U.S.’ climate trajectory but also have global repercussions in the fight to curb fossil fuel emissions and protect communities vulnerable to the compounding impacts of the petrochemical buildout.
In a time when decisive climate action is needed more than ever, building more petrochemical plants is a monumental mistake the U.S. cannot afford to make. The time to act is now.