

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
One campaigner said the cancellation "marks another monumental victory for our planet and future generations, a victory where Indigenous peoples' resistance has been central."
Environmental and Indigenous activists declared Thursday that "geoengineering fails again," welcoming the shutdown of a project that aimed to use "a reflective material to protect and restore Arctic sea ice," which is rapidly disappearing as humanity's reliance on fossil fuels heats the planet.
Noting that "we committed to moving forward only if we could conclusively demonstrate both the safety and effectiveness of our approach," the Arctic Ice Project team confirmed in an online statement that it "will be concluding its research and winding down the organization."
"While our climate impact simulations have shown promising results (with a new scientific paper forthcoming), recent ecotoxicological tests have revealed potential risks to the Arctic food chain," the team said. "Our initial approach was to continue research aimed at addressing these concerns. Upon further reflection, however, the board decided that the combination of these new test results with broad skepticism toward geoengineering, resistance to introducing new materials into the Arctic Ocean, and the increasingly challenging funding environment (and paucity of federal research dollars), the most realistic path was to conclude our research."
"Nature is not a laboratory; it is a living entity we are in relationship with."
Responding in a Thursday statement, Hands Off Mother Earth Alliance global coordinator Coraina de la Plaza said that "the cancellation of the Arctic Ice Project marks another monumental victory for our planet and future generations, a victory where Indigenous peoples' resistance has been central. This outcome reflects the power of community advocacy, and while the fight against geoengineering is far from over, this is a significant step to continue protecting the Arctic against industry greed and vested interests."
Panganga Pungowiyi, climate geoengineering organizer at Indigenous Environmental Network, called the decision "long overdue."
"We are concerned for the community members in Utqiaġvik who were made to spread football fields of this material onto their frozen lake. For years, we stood in defense of Indigenous lands and the sacred ice that has sustained our communities for generations," Pungowiyi explained. "Our concerns about the reckless use of harmful materials were dismissed, yet we knew that the health of our ecosystems and the wisdom of our people must not be overlooked. We continually showed up in defense of free prior and informed consent, and made our presence known."
"We continue to state firmly that nature is not a laboratory; it is a living entity we are in relationship with," the organizer added. "While we find relief in this victory, we remain vigilant against other forms of geoengineering that threaten our sacred spaces. Together, we will continue to educate and empower our communities, standing with our lands, waters, and air for the generations to come."
Silvia Ribeiro, Latin America director at ETC Group, said that "today we celebrate the wisdom, experience, and work of Indigenous peoples and organizations in Alaska that stopped this project and stand in solidarity with their vigilance against similar experiments that are planned in Arctic regions."
Mary Church, geoengineering campaign manager at the Center for International Environmental Law, also framed the development as "a huge victory for the Indigenous communities at the forefront of resistance to the industries and vested interests that are polluting the planet and gambling with our collective future."
"Geoengineering approaches do nothing to address the root causes of the climate crisis and instead delay real solutions, offering a free pass to polluters," she stressed. "Following the recent reaffirmation of the global moratorium on geoengineering at the U.N. biodiversity summit in Colombia, governments need to act to prevent harmful outdoor experiments and the slippery slope to legitimizing deployment. Instead of betting on highly speculative techno-fixes, governments must prioritize an urgent and just transition away from fossil fuels to protect vital Arctic ecosystems."
Benjamin Day, a senior campaigner for climate and energy justice at Friends of the Earth U.S., also looked to the fight ahead.
"The decision to shut down the Arctic Ice Project completes the Geoengineering Hype Cycle that we now see so often: Entrepreneurs swoop into local communities claiming they have a solution to global warming, assuring everyone it's completely safe and ignoring the red flags raised by those with deep knowledge of local ecosystems," Day said. "After countless wasted dollars and press attention, it's revealed the community was right and geoengineering is not a safe or responsible way to address climate change."
"Collectively," he argued, "we must stop enabling this cycle and work towards rapidly and equitably transitioning our communities to sustainable energy and land-use practices."
The winding down of the Arctic Ice Project comes amid global fears about what the recent return of Republican U.S. President Donald Trump—who cozied up to Big Oil executives on the campaign trail and promised to "drill, baby, drill," despite the devastating impacts of fossil fuels—will mean for the future of a planet that last year saw record-shattering temperatures.
Already, Trump has
ditched the Paris climate agreement (again), lifted a freeze on new liquefied natural gas exports, declared a "national energy emergency," and named various fossil fuel allies to key positions. Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Lee Zeldin and Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy took their posts earlier this week, Interior Secretary Doug Burgum was confirmed by the Republican-controlled Senate Thursday evening, and Chris Wright, Trump's pick for energy secretary, awaits confirmation.
"The industry's operations and the use of its products disrupt fragile ecosystems, destroy habitats, and pollute air, water, and soil, pushing countless species to human-induced extinction."
With just a few more days of the United Nations biodiversity summit in Cali, Colombia, 140 organizations collectively called on government representatives to pursue "an immediate halt" to new planet-heating oil and gas projects and "a managed decline of existing activity."
The letter—signed by civil society groups, Indigenous peoples, and social movements—advocates "prioritizing areas of high biodiversity importance" and stresses the need for "a full, fair, fast, funded, and feminist phaseout of all fossil fuels and to halt and reverse biodiversity loss."
"Oil and gas activity threatens biodiversity at every stage—from exploration and production to transportation and end use," the letter states. "The industry's operations and the use of its products disrupt fragile ecosystems, destroy habitats, and pollute air, water, and soil, pushing countless species to human-induced extinction. The risk oil and gas activity poses to biodiversity grows as these operations expand into vulnerable ecosystems."
"Effective biodiversity protection is not possible without halting the expansion of oil and gas activity."
"Places like the Amazon, including the mouth of the Amazon River, are experiencing significant environmental and social impacts from oil and gas activity," the letter notes. "Deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution of water sources are threatening biodiversity in one of the world's most critical ecosystems, and severely disrupting the fundamental human rights and livelihoods of Indigenous peoples."
The coalition—which includes Amazon Watch, Center for International Environmental Law, Earthjustice, Greenpeace, Oil Change International, Waterkeepers Alliance, and World Wide Fund for Nature—has a list of recommendations for attendees of the 16th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (COP16).
The groups want summit attendees to "recognize the threat that oil and gas activity poses to all biodiversity, particularly in areas of high biodiversity importance." Regarding such vital areas, they want attendees to "identify concrete actions currently being taken and that will be taken in the future to immediately reduce oil and gas activities" as well as "adopt a decision to immediately halt" new fossil fuel activities in such spaces.
The organizations are also calling for a "fossil fuel-free zone" in the Amazon and prioritizing "the protection of environmental and human rights defenders." According to Global Witness, at least 196 such activists were killed in 2023 alone, bringing the total since 2012 to 2,106.
Additionally, the coalition wants COP16 attendees to "enhance equitable international cooperation to ensure that countries with the greatest historical responsibility for driving biodiversity loss and the production and use of fossil fuels move first and fastest to halt the expansion of oil and gas activity, and pursue new enforceable international mechanisms, such as a fossil fuel nonproliferation treaty."
"Faced with an unprecedented planetary crisis, the time is now for parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity to fulfill their legal obligations and reaffirm their mandate to protect global biodiversity," the letter argues. "Effective biodiversity protection is not possible without halting the expansion of oil and gas activity, and eliminating the threat from ongoing oil and gas activity, particularly in areas of high biodiversity importance."
COP16 kicked off in Cali on October 21 and is set to wrap up on November 1. Reutersreported Tuesday that "countries were at an impasse over how to fund conservation and other key decisions... with nations pledging millions of dollars rather than the billions needed."
At COP15 in late 2022, countries finalized the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, which aims to protect 30% of all land and water vital to species and ecosystems by 2030. To reach that goal, "protected and conserved areas must almost double in area on land and more than triple in the ocean, the U.N. Environment Program World Conservation Monitoring Center and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) said Monday.
The IUCN also
warned Monday as part of its "Red List" that more than 16,000 of 47,000 analyzed tree species worldwide are at risk of extinction. The report followed similar warnings of wildlife population decline released ahead of COP16.
"The petrochemical industry and its toxic products pose an urgent threat to human health and the global climate," a campaigner said.
Environmental and policy groups on Tuesday called for financial institutions to stop funding the U.S. petrochemical industry.
Break Free from Plastic, Friends of the Earth, the Center for International Environmental Law (CIEL), and the Texas Campaign for the Environment issued a 39-page report, Exiting Petrochemicals, that they called a "guide" for financial institutions to divest from the industry.
Petrochemicals are made from fossil fuels and are the basis for a wide array of industrial feedstocks and end products, mostly in plastics or fertilizers. The products drive climate change and harm public health throughout their life cycle, from the frontline communities—disproportionately marginalized and low-income—where fuels are extracted to the oceans and human bodies where microplastics, for example, end up.
The report calls for financial institutions—banks, investment firms, and insurance companies—to stop funding fracking, rapidly phase out all fossil fuel financing, and require petrochemical clients to publicly release transition plans. It also calls for an immediate halt on the financing of new petrochemical projects, about 120 of which are currently planned in the U.S., mostly in the Gulf and the Ohio River Valley.
"The communities most impacted by these developments, often low-income and communities of color, bear the brunt of pollution and health risks," Sharon Lavigne, executive director of RISE St. James, a campaign group in Louisiana, said in a statement.
"We must hold financial institutions accountable for their role in financing these harmful projects," Lavigne added. "It's time to stop funding environmental racism and start investing in a cleaner, safer future for everyone."
Diane Wilson, the executive director of the San Antonio Bay Estuarine Waterkeeper and a fourth-generation fisher, said the industry had already had a negative impact on her area.
"Given the terrible damage that I have seen corporations like Formosa Plastics do to communities, workers, fisheries, bays, and fishermen, the line has to be drawn: No more funding for plastics and petrochemicals!" she said.
Brandon Marks, a CIEL campaigner, summarized the problems the report seeks to address: "The petrochemical industry and its toxic products pose an urgent threat to human health and the global climate."
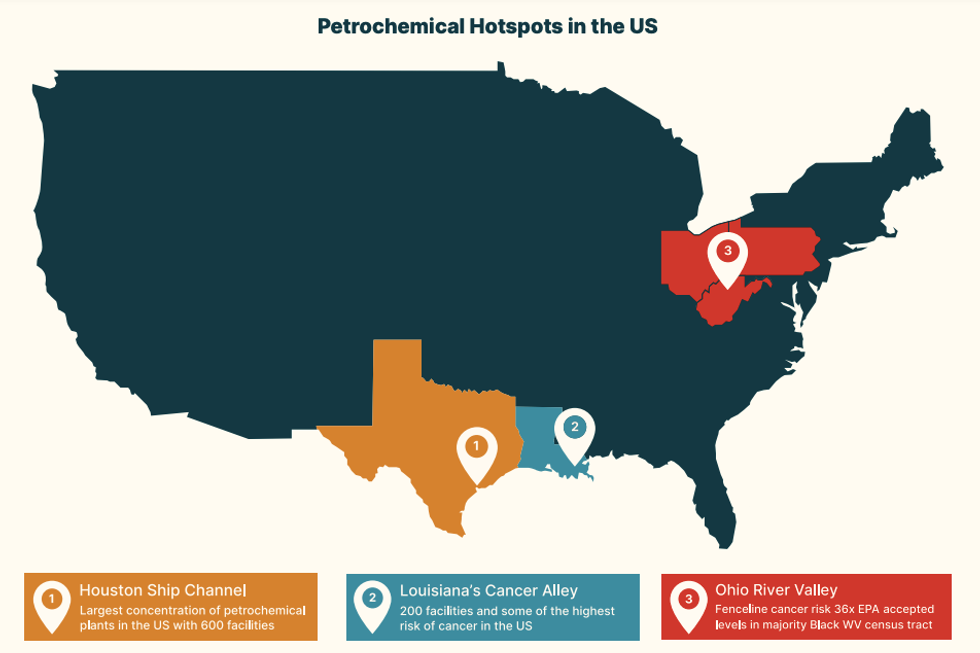
Primary plastics production accounted for 5.3% of global greenhouse gas emissions as of 2019—more than commercial aviation and international shipping combined, according to the report.
Fertilizers are also a major emissions source, especially those used in cornfields. Synthetic nitrogen fertilizers derived from fossil fuels account for an estimated 2-5% of total global emissions.
In total, the U.S. petrochemical industry alone releases roughly the emissions equivalent of 40 coal-fired power plants every year, the report says.
The climate impact, however, is only part of the problem, as the report details.
"Petrochemical production releases carcinogenic and other highly toxic substances into the air, exposing fenceline communities to higher risks of cancer, leukemia, reproductive and developmental problems, nervous system impairment, and genetic impacts," the authors wrote in the executive summary.
"Petrochemical production also pollutes waterways with contaminated wastewater," they continued. "In fact, Formosa Plastics was fined $50 million in 2019 for illegally discharging plastic pollution into Texas waterways and another $19.2 million as of June 2024 for continuing violations."
Fossil fertilizers also pose major risks, endangering farmworkers, polluting drinking water, and causing dead zones in marine environments like the Gulf of Mexico, the report says.
Two-thirds of the people living on the fenceline of petrochemical projects are from marginalized racial backgrounds, making these groups disproportionately represented—they make up only 39% of the U.S. population, according to the report.
The authors also put forth the business case against financing the petrochemical industry, arguing that new regulations and decreased demand will make petrochemical plants stranded assets.
"Choosing to finance and insure these projects is not just irresponsible; it's a poor investment," Marks of CIEL said. "Banks, insurers, and investors must stop financing petrochemicals now."