"Nations must collectively commit to cutting 42% off annual greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and 57% by 2035 in the next round of Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)—and back this up with rapid action—or the Paris agreement's 1.5°C goal will be gone within a few years," UNEP warned.
"Failure to increase ambition in these new NDCs and start delivering immediately would put the world on course for a temperature increase of 2.6-3.1°C over this century," the agency said. "This would bring debilitating impacts to people, planet, and economies."
UNEP said "solar, wind, and forests" have the potential to help the world "get on a 1.5°C pathway." However, "sufficiently strong NDCs would need to be backed urgently by a whole-of-government approach, measures that maximize socioeconomic and environmental co-benefits, enhanced international collaboration that includes reform of the global financial architecture, strong private sector action, and a minimum six-fold increase in mitigation investment."
"G20 nations, particularly the largest-emitting members, would need to do the heavy lifting," the agency added.
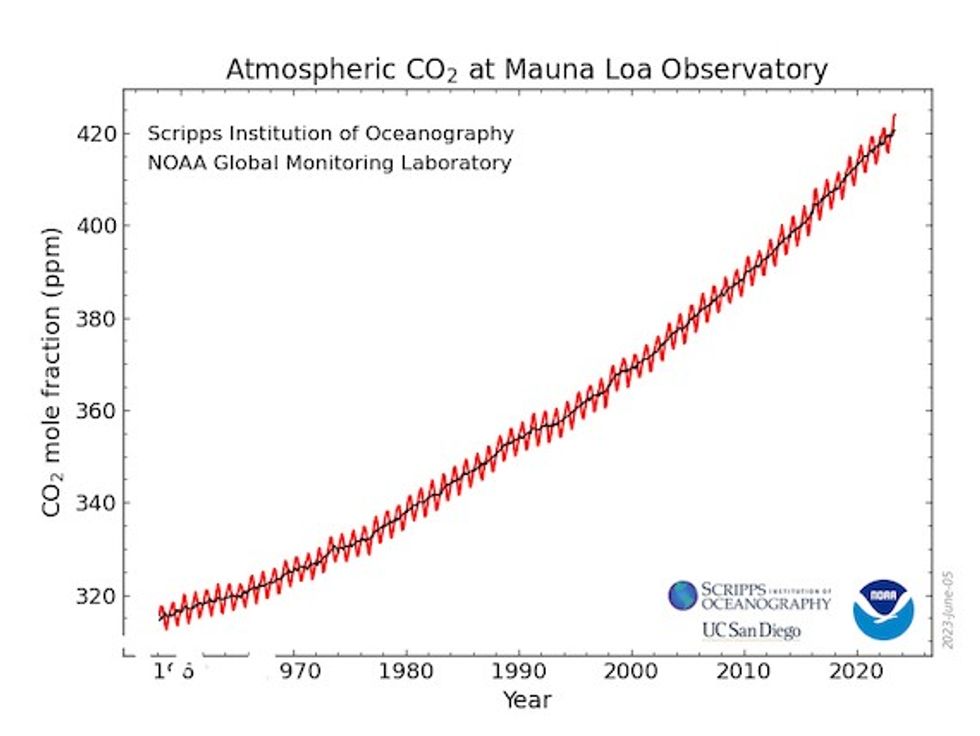
The task is daunting—according to the report, human emissions of greenhouse gases—CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases—reached a record 57.1bn tons of CO2 equivalent (GtCO2e) last year.
"The emissions gap is not an abstract notion," U.N. Secretary-General António Guterres stressed in a video message on the UNEP report. "There is a direct link between increasing emissions and increasingly frequent and intense climate disasters."
"Around the world, people are paying a terrible price," he continued. "Record emissions mean record sea temperatures supercharging monster hurricanes; record heat is turning forests into tinder boxes and cities into saunas; record rains are resulting in biblical floods."
"Today's Emissions Gap report is clear: We're playing with fire; but there can be no more playing for time," Guterres added. "We're out of time. Closing the emissions gap means closing the ambition gap, the implementation gap, and the finance gap. Starting at COP29."
The U.N. chief was referring to the United Nations Climate Change Conference, which is set to take place next month in Baku, Azerbaijan—a nation that is "aggressively" expanding fossil fuel production.
UNEP Executive Director Inger Andersen said in a statement:
Climate crunch time is here. We need global mobilization on a scale and pace never seen before—starting right now, before the next round of climate pledges—or the 1.5°C goal will soon be dead and well below 2°C will take its place in the intensive care unit. I urge every nation: No more hot air, please. Use the upcoming COP29 talks in Baku, Azerbaijan, to increase action now, set the stage for stronger NDCs, and then go all-out to get on a 1.5°C pathway.
Even if the world overshoots 1.5°C—and the chances of this happening are increasing every day—we must keep striving for a net-zero, sustainable, and prosperous world. Every fraction of a degree avoided counts in terms of lives saved, economies protected, damages avoided, biodiversity conserved, and the ability to rapidly bring down any temperature overshoot.
Climate scientists and green groups expressed alarm over the UNEP report.
"The Emissions Gap Report is yet another clear warning about what needs to be done and fast," Andreas Sieber, associate director of policy and campaigns at 350.org, said in a
statement. "Last year at COP28, nations agreed to transition away from fossil fuels. The report makes it crystal clear that governments must translate this decision into action in their national climate pledges if they are serious about the just energy transition."
Greenpeace International climate politics expert Tracy Carty
said that "for 15 years, the UNEP has been sounding the alarm on the great chasm between political will for climate action and the worsening emissions trajectory fuelling rising temperatures."
"These reports are a historical litany of negligence from the world's leaders to tackle the climate crisis with the urgency it demands, but it's not too late to take corrective action," Carty continued. "We challenge leaders to embark on wholesale change in their 2035 climate plans, to come to COP29 prepared to finance climate action and to make up for lost time."
Rachel Cleetus, policy director and a lead economist in the Climate and Energy Program at the Union of Concerned Scientists, issued a statement arguing that the new UNEP report "forcefully confirms that nations' efforts to cut heat-trapping emissions have been grossly insufficient to date."
"Global heating records are being topped year after year, and people and ecosystems worldwide are suffering the devastation of unrelenting climate change disasters and increasingly irreversible impacts," she noted. "To put it bluntly, decades of inadequate action have put the 1.5°C goal further out of reach and world leaders are failing their people. The consequences are profound—but the policy choices decided now are as crucial as ever to limit future harm."
Cleetus continued:
The best way forward is to implement sweeping changes to the global energy system by phasing out the destructive products fossil fuel companies are peddling and investing big in renewable energy solutions to sharply curtail heat-trapping emissions. Also urgent are scaled-up investments in climate resilience to cope with impacts already locked in. Rich, high-emitting nations—including the United States—are most responsible for these calamitous circumstances. Those living in climate-vulnerable, low-income countries that contributed very little to the fossil fuel pollution driving this crisis need more than hollow words; they need wealthy countries and other major emitters to live up to their responsibilities.
"At the upcoming U.N. climate talks, wealthy nations must significantly grow the amount of climate financing available to ensure all countries can slash their global warming emissions and prepare for the more frequent and severe climate impacts that are the punishing consequence of a warming world," Cleetus added.