

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
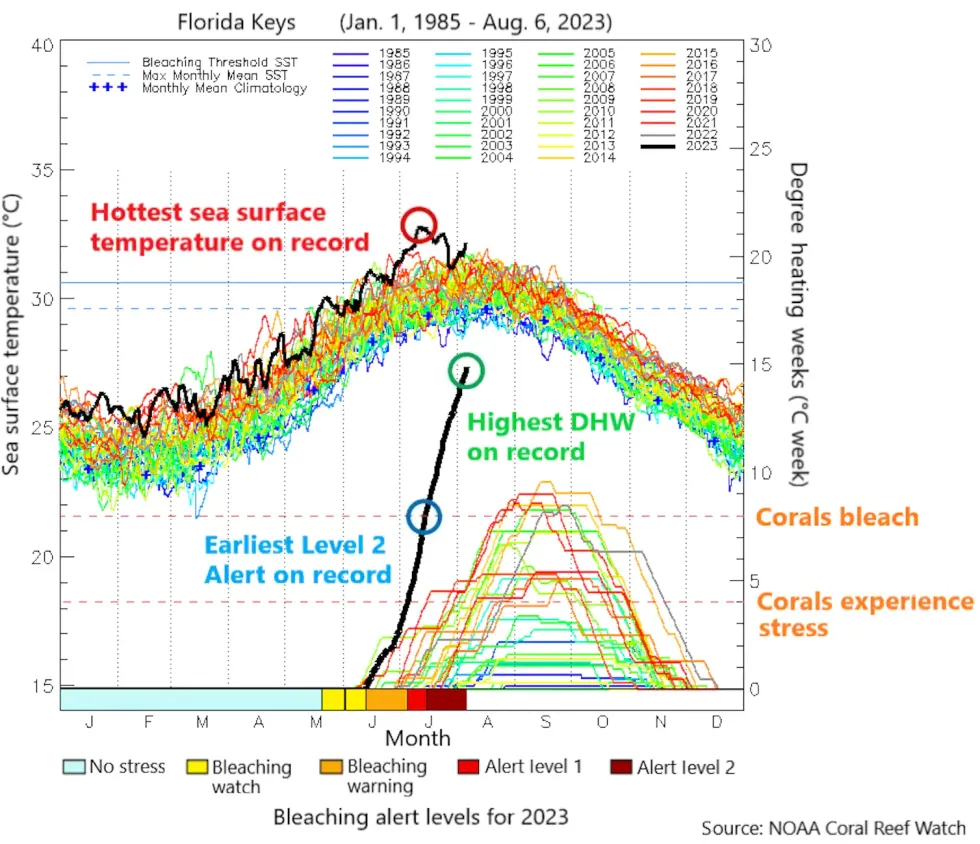
This year, the Florida Keys reached an alert level 2, indicating extreme risk of bleaching, about six weeks earlier than normal.
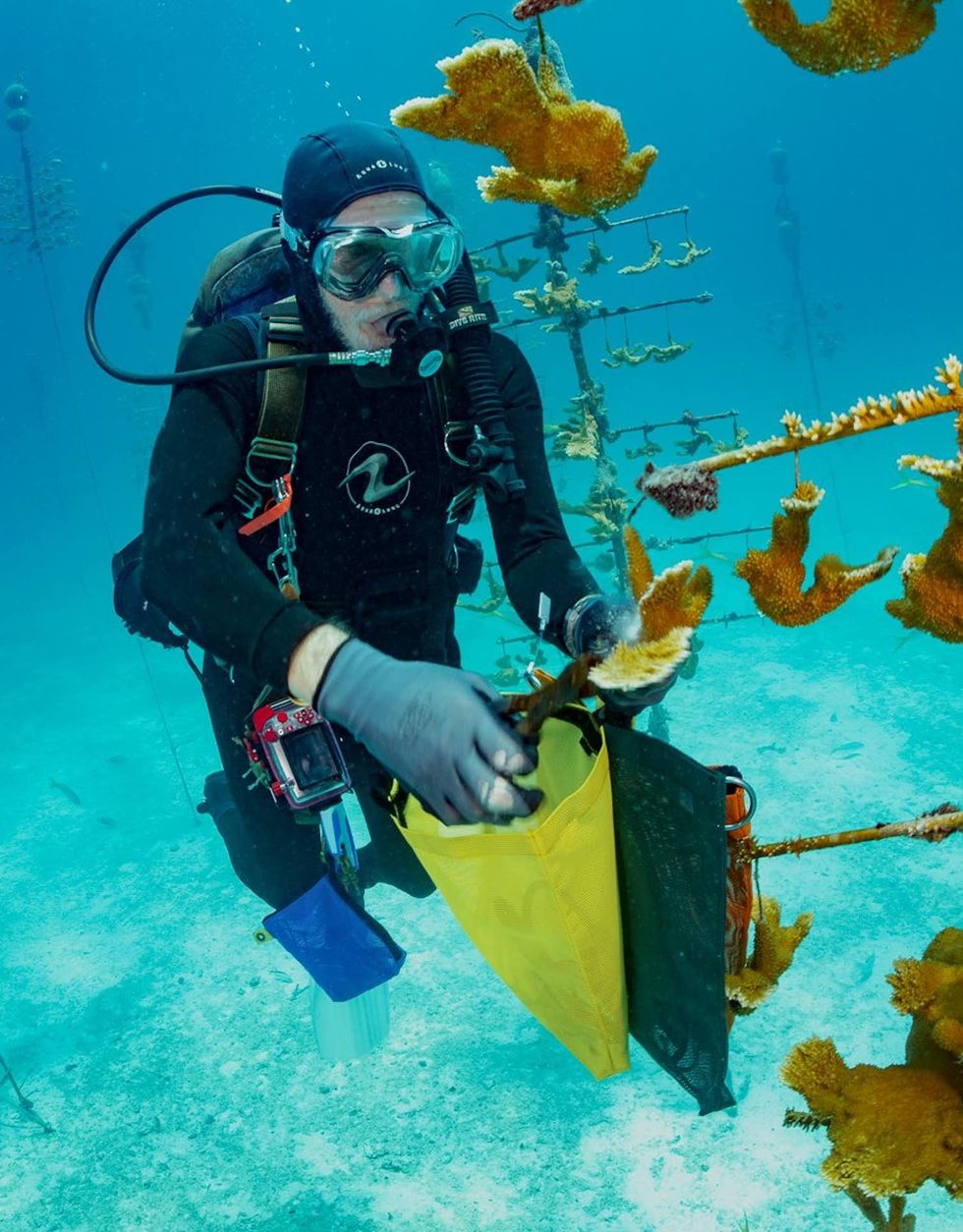
Armed with scrub brushes, young scuba divers took to the waters of Florida’s Alligator Reef in late July to try to help corals struggling to survive 2023’s extraordinary marine heatwave. They carefully scraped away harmful algae and predators impinging on staghorn fragments, under the supervision and training of interns from Islamorada Conservation and Restoration Education, or I.CARE.
Normally, I.CARE’s volunteer divers would be transplanting corals to waters off the Florida Keys this time of year, as part of a national effort to restore the Florida Reef. But this year, everything is going in reverse.
As water temperatures spiked in the Florida Keys, scientists from universities, coral reef restoration groups, and government agencies launched a heroic effort to save the corals. Divers have been in the water every day, collecting thousands of corals from ocean nurseries along the Florida Keys reef tract and moving them to cooler water and into giant tanks on land.
Marine scientist Ken Nedimyer and his team at Reef Renewal USA began moving an entire coral tree nursery from shallow waters off Tavernier to an area 60 feet deep and 2°F (1.1°C) cooler. Even there, temperatures were running about 85 to 86°F (30°C).

Their efforts are part of an emergency response on a scale never before seen in Florida.
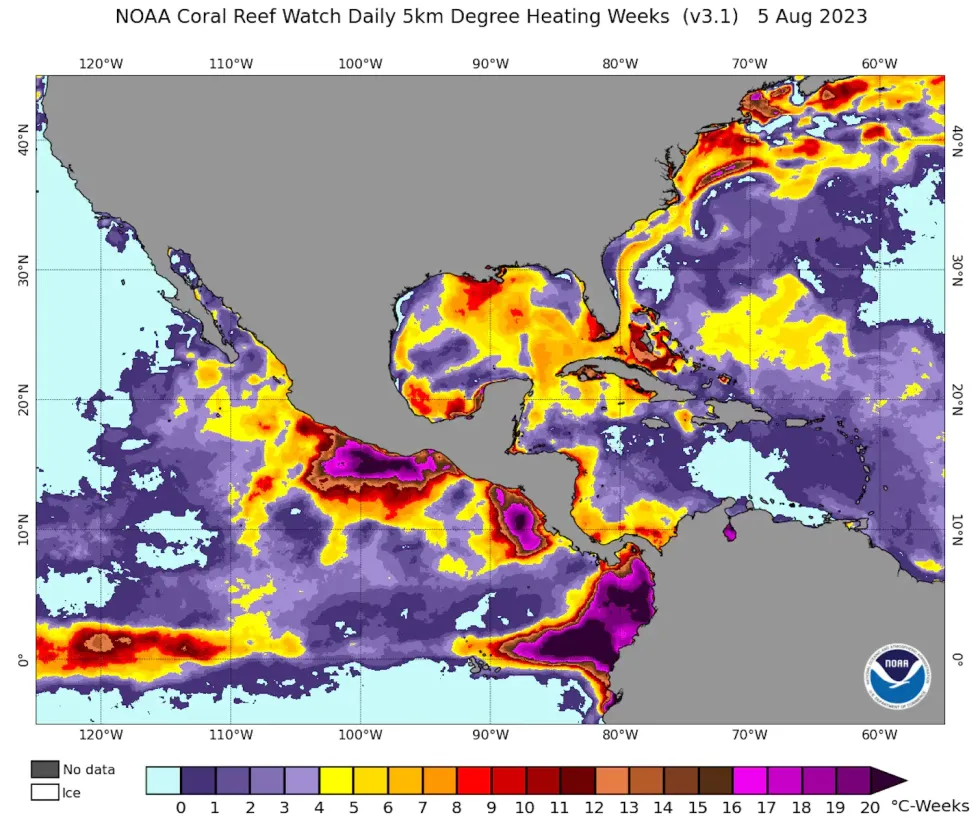
The Florida Reef—a nearly 350-mile arc along the Florida Keys that is crucial to fish habitat, coastal storm protection, and the local economy—began experiencing record-hot ocean temperatures in June 2023, weeks earlier than expected. The continuing heat has triggered widespread coral bleaching.
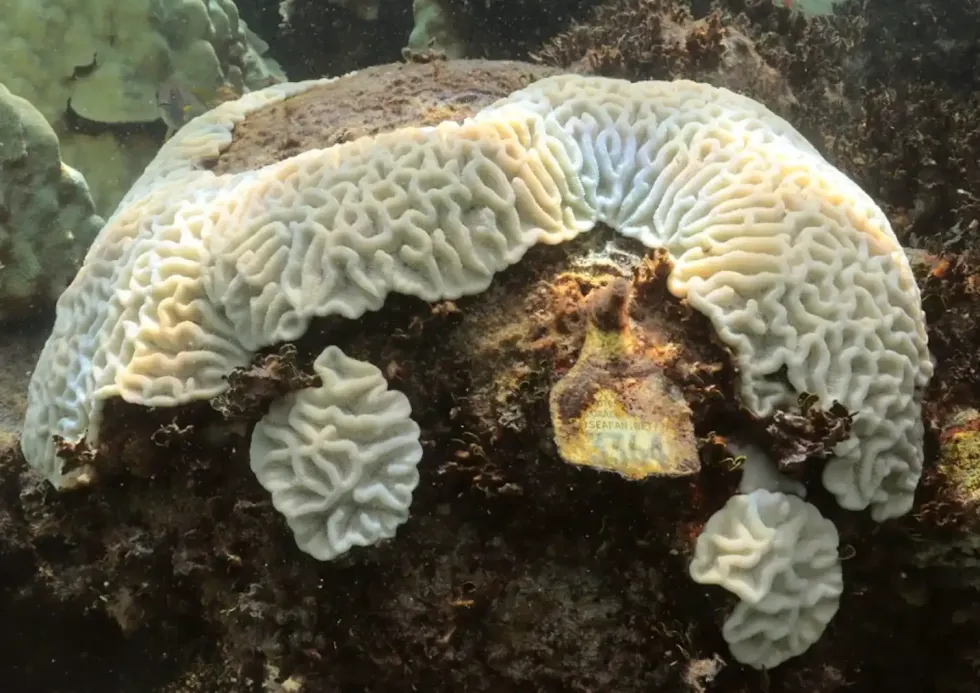

While corals can recover from mass bleaching events like this, long periods of high heat can leave them weak and vulnerable to disease that can ultimately kill them.
That’s what scientists and volunteers have been scrambling to avoid.
The heartbeat of the reef
The Florida Reef has struggled for years under the pressure of overfishing, disease, storms, and global warming that have decimated its live corals.
A massive coral restoration effort—the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Mission: Iconic Reef—has been underway since 2019 to restore the reef with transplanted corals, particularly those most resilient to the rising temperatures. But even the hardiest coral transplants are now at risk.
Reef-building corals are the foundation species of shallow tropical waters due to their unique symbiotic relationship with microscopic algae in their tissues.
During the day, these algae photosynthesize, producing both food and oxygen for the coral animal. At night, coral polyps feed on plankton, providing nutrients for their algae. The result of this symbiotic relationship is the coral’s ability to build a calcium carbonate skeleton and reefs that support nearly 25% of all marine life.
Unfortunately, corals are very temperature sensitive, and the extreme ocean heat off South Florida, with some reef areas reaching temperatures in the 90s, has put them under extraordinary stress.
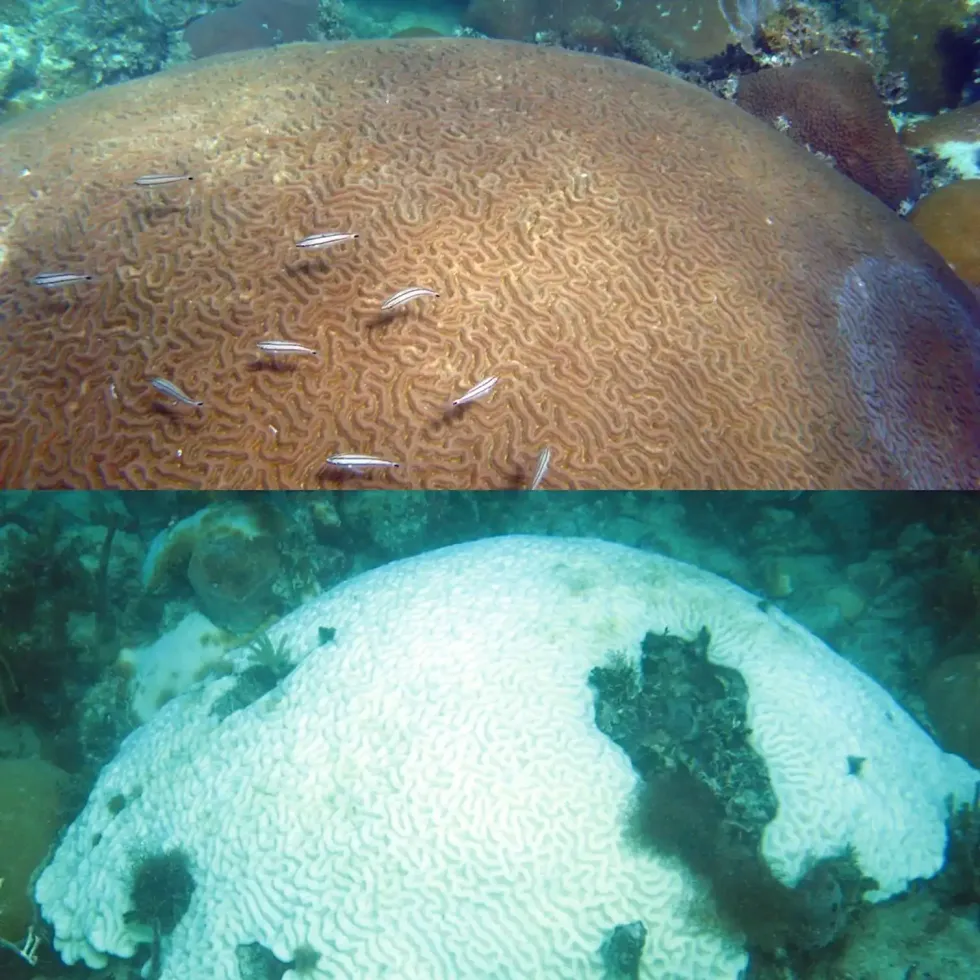

When corals get too hot, they expel their symbiotic algae. The corals appear white—bleached—because their carbonate skeleton shows through their clear tissue that lack any colorful algal cells.
Corals can recover new algal symbionts if water conditions return to normal within a few weeks. However, the increase in global temperatures due to the effects of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities is causing longer and more frequent periods of coral bleaching worldwide, leading to concerns for the future of coral reefs.
A MASH unit for corals
This year, the Florida Keys reached an alert level 2, indicating extreme risk of bleaching, about six weeks earlier than normal.
The early warnings and forecasts from NOAA’s Coral Reef Watch Network gave scientists time to begin preparing labs and equipment, track the locations and intensity of the growing marine heat, and, importantly, recruit volunteers.
At the Keys Marine Laboratory, scientists and trained volunteers have dropped off thousands of coral fragments collected from heat-threatened offshore nurseries. Director Cindy Lewis described the lab’s giant tanks as looking like “a MASH unit for corals.”
Volunteers there and at other labs across Florida will hand-feed the tiny creatures to keep them alive until the Florida waters cool again and they can be returned to the ocean and eventually transplanted onto the reef.
Protecting corals still in the ocean
I.CARE launched another type of emergency response.
I.CARE co-founder Kylie Smith, a coral reef ecologist and a former student of mine in marine sciences, discovered a few years ago that coral transplants with large amounts of fleshy algae around them were more likely to bleach during times of elevated temperature. Removing that algae may give corals a better chance of survival.
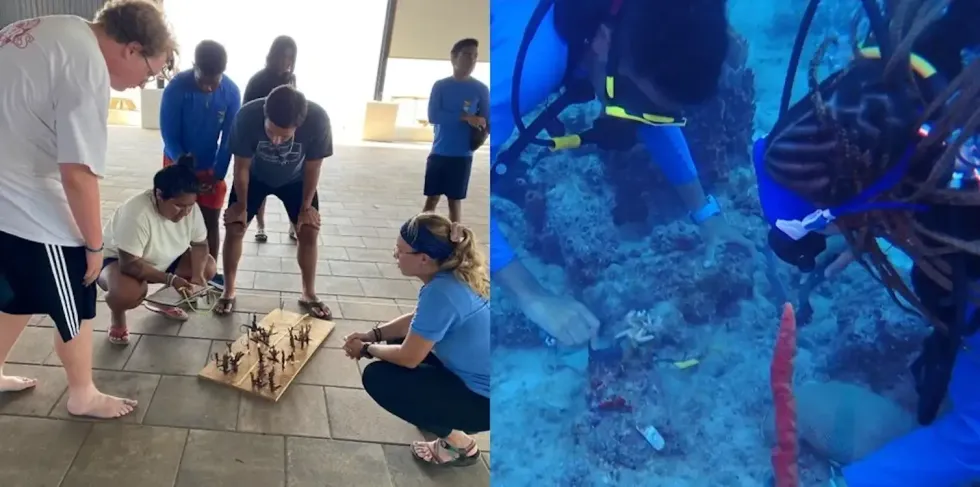

Smith’s group typically works with local dive operators to train recreational divers to assist in transplanting and maintaining coral fragments in an effort to restore the reefs of Islamorada. In summer 2023, I.CARE has been training volunteers, like the young divers from Diving with a Purpose, to remove algae and coral predators, such as coral-eating snails and fireworms, to help boost the corals’ chances of survival.
Monitoring for corals at risk
To help spot corals in trouble, volunteer divers are also being trained as reef observers through Mote Marine Lab’s BleachWatch program.
Scuba divers have long been attracted to the reefs of the Florida Keys for their beauty and accessibility. The lab is training them to recognize bleached, diseased, and dead corals of different species and then use an online portal to submit bleach reports across the entire Florida Reef.
The more eyes on the reef, the more accurate the maps showing the areas of greatest bleaching concern.
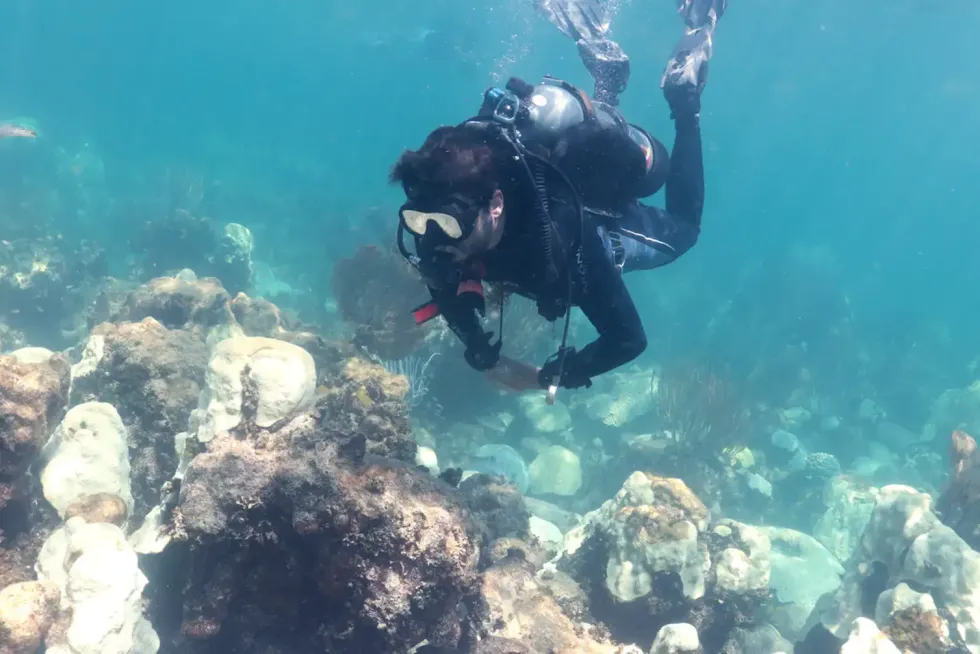

Rebuilding the reef
While the marine heatwave in the Keys will inevitably kill some corals, many more will survive.
Through careful analysis of the species, genotypes, and reef locations experiencing bleaching, scientists and practitioners are learning valuable information as they work to protect and rebuild a more resilient coral reef for the future.
That is what gives hope to Smith, Lewis, Nedimyer, and hundreds of others who believe this coral reef is worth saving. Volunteers are crucial to the effort, whether they’re helping with coral reef maintenance, reporting bleaching, or raising the awareness of what is at stake if humanity fails to stop warming the planet.
In what is expected to be a grim reading, the world's leading climate scientists will give their latest assessment about the dangers of global warming next week.
They will warn us not only what damage the burning of fossil fuels is already causing across the globe, but also shed light on the future climate impacts we can expect during the lifetimes of children born today, depending on the choices we make now and in the future.
If you can't wait, check out the video from the World Bank, which sums up in two minutes what the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) will elaborate on in more than 2,000 pages after finalising its study in Japan this week.
The report follows another wave of weird weather extremes around the world, from the blistering heatwaves in Australia or ferociously cold weather in North America to flooding in the UK and the devastating Supertyphoon Haiyan in the Philippines. Millions of people suffered as a result, losing homes, livelihoods - on top of the lives lost.
These events have not happened in isolation.
Last year the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) said the world experienced unprecedented high-impact climate extremes during 2001-2010 - the warmest decade since the start of modern measurements in 1850. It was dubbed the decade of climate extremes.
Is this climate change slipping out of control?
Well, the first part of the IPCC's fifth Assessment Report, launched last September, outlined how our greenhouse gas pollution has already warmed the atmosphere and oceans, melted glaciers, raised sea levels, changed water cycles and worsened some extreme weather events.
There also are alarming signs of accelerating impacts. In the years 2002-2011, the Greenland ice sheet was losing mass about six times faster on average than the preceding decade. Similarly, the Antarctic ice sheet lost mass five times faster.
Since 1993 sea levels have risen twice as fast than they did in the past century on average, and sea ice extent in the Arctic diminished significantly faster than projected.
So do we really need yet another warning? Will it make any difference?
The difference this time is that a key focus in the upcoming IPCC report is on choice.
Either we reduce and manage the risks ahead and do what's needed to keep warming as far below 2 degrees Celsius as possible, or we continue to do too little too late, drifting from crisis to crisis and on towards a disastrous 4 degrees world. The IPCC will paint a picture of both these possible futures.
Today we are in a situation where governments have promised to keep warming below 2 degrees Celsius but are heading instead towards a 4 degree world. They are neither preparing for a 2 degree nor a 4 degree world, trying to ignore the megatrend of climate change.
The truth is they can't ignore it. That's what the UK Environment Secretary Owen Paterson, a climate change denier, had to learn recently in the middle of the devastating UK floods.
In a climate-constrained world there is no business as usual. Building new coal plants with massive water footprints in areas that are already suffering from water shortage, soon to be exacerbated by climate change, is just not going to work.
Not everyone is hiding their head in the sand though. Millions of people around the world are already facing the reality of climate change and responding to it. They are preparing for a world that phases out fossil fuels and they are already making a difference.
Coal plants are being cancelled and self-controlled renewable energy systems installed. The fossil fuel divestment campaign is swiftly growing and people are standing up in millions to protect our forests, the Arctic and other riches threatened by climate change.
We can still prevent catastrophic climate change, but we need to get on with it.
Click here for a Greenpeace preview of the IPCC WG II report.
Click here for a briefing on Japan's climate and energy challenge.
World Could Be 4 Degrees Hotter By End of This Centuryhttps://www.worldbank.org/climatechange - The World Bank warns that rising temperatures could be disastrous, and urges more ...