It’s called sportswashing, a riff on the term greenwashing. Companies sponsor leagues and teams to present themselves as good corporate citizens, increase visibility, and build public trust. According to a 2021 Nielsen study, 81% of fans completely or somewhat trust companies that underwrite sport teams, second only to the trust they have for friends and family. By sponsoring a team, companies increase the chance that fans will form the same bond with their brand that they have with the team.
Baseball club owners are much more concerned about their bottom line than their sponsors’ climate impacts.
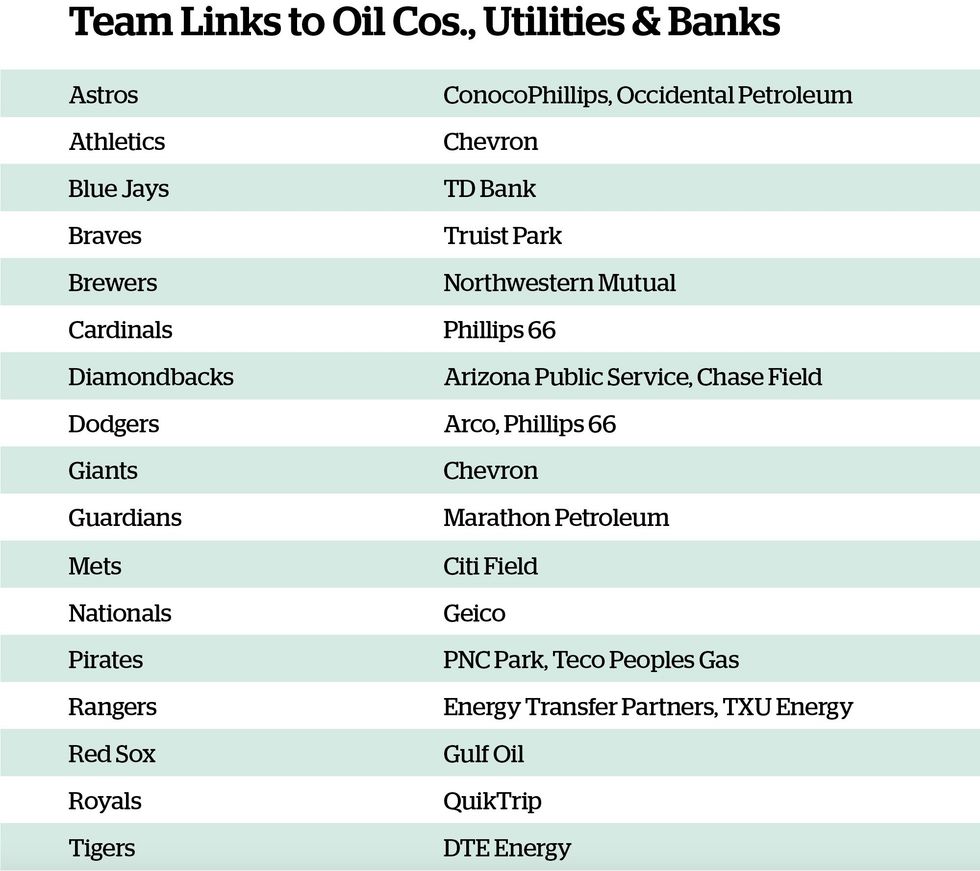
Baseball teams are not alone in their pursuit of petrodollars. At least 35 U.S. pro basketball, football, hockey, and soccer teams have similar sponsorship deals that afford companies a range of promotional perks, from billboards and jersey logos to community outreach projects and facility naming rights, according to a survey conducted last fall by UCLA’s Emmett Institute on Climate Change and the Environment. U.S. sports leagues and teams also partner with banks and insurance companies that invest billions of dollars annually in coal, oil, and gas companies, all to the detriment of public health and the environment.
Most baseball aficionados are likely unaware that their favorite team is going to bat for the very companies and banks that are destroying the climate, but a growing number of fans in New York and Los Angeles are calling out the Mets and Dodgers, demanding that they sever their ties to the fossil fuel industry. And once they know, will fans in other MLB cities remain on the sidelines?
Shilling for the Biggest Polluters
Oil, gas, and coal are largely responsible for the carbon pollution driving up world temperatures and triggering more dangerous extreme weather events. Last year was yet another record hot year, and the last 10 years have been the hottest in nearly 200 years of recordkeeping, according to the World Meteorological Organization. Those warmer temperatures certainly played a role in producing the 27 weather and climate disasters in the United States last year that caused at least $1 billion in damages, one less than the record set in 2023. And just this week, violent storms and tornadoes ripped through a swath of the nation’s midsection in what The Associated Press said could be a “record-setting period of deadly weather and flooding.”
Regardless, baseball club owners are much more concerned about their bottom line than their sponsors’ climate impacts. But with today’s annual MBL payrolls averaging $157 million, it is not hard to understand why teams pursue corporate sponsorships.

The team with the highest payroll—the Los Angeles Dodgers at $321 million—has a longtime partnership with Phillips 66, owner of 76 gas stations, whose orange-and-blue logo hovers above both Dodger stadium scoreboards and is scattered throughout the facility. Phillips 66, which also sponsors the St. Louis Cardinals, is among the top 10 U.S. air and surface water polluters in total pounds, according to the 2024 edition of Political Economy Research Institute’s “Top 100 Polluter Indexes,” and the 14th-largest carbon polluter, emitting 30.2 million metric tons in 2022.
Arco, owned by Marathon Petroleum, also advertises in Dodger Stadium. The country’s largest oil refiner with more than 7,000 Marathon and Arco gas stations nationwide, Marathon Petroleum is among the top 20 air, surface water, and carbon polluters in the country, according to PERI’s 2024 report, and the company and its subsidiaries have been fined more than $900 million for federal environmental violations since 2014.
The Findlay, Ohio-based company has been one of the Cleveland Guardians’ major corporate sponsors since 2021, and the team has been wearing Marathon Petroleum’s logo on their sleeves since the summer of 2023. The logo also enjoys prime placement in the Guardians’ ballpark and, as part of the uniform patch agreement, it is featured on the souvenir jerseys given to fans on two game days every season through 2026.
The Guardians are not the only team that has inked an oil patch deal. The Houston Astros (Oxy), Kansas City Royals (QuikTrip gas stations), and Texas Rangers (Energy Transfer) also display oil industry logos on their sleeves.
Both Oxy—Occidental Petroleum’s nickname—and the Astros’ other oil industry sponsor, ConocoPhillips, are headquartered in Houston, home to more than 400 oil and petrochemical facilities and among the 10 worst places in the country for air pollution. Occidental is one of the top 30 U.S. air polluters, 40 surface water polluters, and 60 carbon emitters, releasing 10.5 million metric tons of heat-trapping gases in 2022, according to PERI’s 2024 report. ConocoPhillips, meanwhile, came in 88th in PERI’s top 100 carbon polluters list.
Fossil fuel-based utilities also partner with MLB teams. Detroit’s local electric utility DTE, for instance, sponsors the Tigers. More than 40% of DTE’s electricity comes from coal, another 26% comes from fossil gas, and only 12% comes from wind and solar. Although the company is committed to reducing its reliance on coal over the next decade, it plans to replace it with fossil gas, not renewables.
Shilling for Climate Crisis Financiers
Seven teams—and the league itself—have commercial tie-ins with financial institutions that have major fossil fuel industry investments.
The Milwaukee Brewers wear Northwestern Mutual patches on their sleeves. As of last year, the insurance company had $12.17 billion invested in 146 fossil fuel companies, including ExxonMobil, Marathon Petroleum, and Shell, according to a 2024 report by the German environmental nonprofit Urgewald. Meanwhile, the Toronto Blue Jays’ patch sponsor, TD Bank, had nearly twice that amount invested in fossil fuels last year. The Toronto-based bank sunk $21.37 billion in 201 fossil fuel companies, including ExxonMobil and Chevron, which, by the way, sponsors the Sacramento Athletics and San Francisco Giants.
The Washington Nationals partner with Geico, which underwrites a mascot race featuring U.S. presidents running around the outfield warning track every home game. Geico is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway, a multinational conglomerate that, as of last year, had investments of a whopping $95.8 billion in Chevron, Occidental Petroleum, and six other fossil fuel companies.
The other four teams—the Braves, Diamondbacks, Mets and Pirates—have lucrative, multiyear stadium-naming-rights agreements with oil-soaked banks.
- The Braves play in Truist Park just outside of Atlanta. Truist Financial, borne out of the 2019 merger between BB&T and Sun Trust banks, had $1.89 billion invested in Chevron, ExxonMobil, and 100 other fossil fuel companies as of last year. In 2017, Truist predecessor Sun Trust spent $250 million on a 25-year naming rights deal.
- Chase Field in downtown Phoenix is the home of the Arizona Diamondbacks. JPMorgan Chase’s predecessor Bank One spent $66.4 million for the naming rights for 30 years when the stadium opened in 1998, and when JPMorgan Chase bought Bank One in 2004, the facility’s name changed to Chase Field. The biggest financier of fossil fuels worldwide from 2016—when the Paris climate accord went into effect—through 2023, JPMorgan Chase had $89.33 billion invested in fossil fuel companies last year.
- Citigroup paid $400 million for the honor of having the Mets call its then-new ballpark Citi Field for 20 years, from 2009 to 2029. The second-largest financier of fossil fuels between 2016 and 2023, Citigroup had investments totaling $4.37 billion in 150 fossil fuel companies last year.
- The Pirates’ PNC Park is named after the PNC bank, which paid $30 million for the stadium to bear its name from 2001, when it opened, though 2021. The Pirates and the bank extended their agreement until 2031 for an undisclosed sum. Last year, PNC Financial Services had $3.69 billion invested in 147 fossil fuel companies.
Finally, official MLB sponsors include two insurance companies—the aforementioned Berkshire Hathaway subsidiary Geico and New York Life—that have sizeable fossil fuel portfolios. Last year, New York Life had investments of $11.76 billion in 234 companies, including Duke Energy and the Southern Company.
More Fans Are Crying Foul
Last June, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres castigated coal, oil, and gas companies—dubbing them the “godfathers of climate chaos” for spreading disinformation—and called for a worldwide ban on fossil fuel advertising. He also urged ad agencies to refuse fossil fuel clients and companies to stop taking their ads. So far, more than 1,000 advertising and public relations agencies worldwide have pledged to refuse working for fossil fuel companies, their trade associations, and their front groups.
Major League Baseball is behind the curve, but fans, environmentalists, and public officials in New York and Los Angeles are trying to bring their teams up to speed.
Two years ago, a coalition of groups joined New York City Public Advocate Jumaane Williams to urge Mets owner Steven Cohen to change the name of Citi Field. “Citi doesn’t represent the values of Mets fans or NYC,” Williams wrote in a tweet. “If they refuse to end their toxic relationship with fossil fuels, the Mets should end their partnership with Citi.”
Activists in New York and Los Angeles are hoping that more public officials—and more fans—will step up to the plate and pressure the teams to do the right thing.
Last summer, the groups that led the effort to persuade the Mets to drop Citigroup, including New York Communities for Change, Stop the Money Pipeline, and Climate Defenders, targeted Citigroup directly with their Summer of Heat on Wall Street campaign calling on the company to stop financing fossil fuels altogether.
In Los Angeles, more than 80 public interest groups, scientists, and environmental advocates signed an open letter last August calling on the Dodgers to cut its ties with Phillips 66. “Using tactics such as associating a beloved, trusted brand like the Dodgers with enterprises like 76,” the letter states, “the fossil fuel industry has reinforced deceitful messages that ‘oil is our friend,’ and that ‘climate change isn’t so bad.’” Since then, more than 28,000 Dodger fans have signed the letter, and last week the Sierra Club’s Los Angeles chapter held a rally outside of Dodger Stadium on opening day demanding that owner Mark Walter end his team’s Phillips 66 sponsorship deal.
The campaign has received support from some local public officials. Lisa Kaas Boyle, a former deputy district attorney in Los Angeles County’s environmental crimes division, was quoted in a L.A. Sierra Club press release in January. “Booting Big Oil out of baseball is up to the fans, because team owners won’t take responsibility,” she said. “This isn’t abstract. Bad air quality from wildfires has forced MLB teams to move games, a hurricane ripped the roof off of [Tampa’s] Tropicana Field, and the Dodgers had to give out free water in 103°F heat last summer. It’s almost becoming too hot to watch at Chavez Ravine.”
State Sen. Lena Gonzalez (D-33), a lifelong Dodger fan, also endorsed the campaign. “Continuing to associate these [fossil fuel] corporations with our beloved boys in blue is not in our community or the planet’s best interest,” she recently told the City News Service, a Southern California news agency. “Ending the sponsorship with Phillips 66 would send the message that it’s time to end our embrace of polluting fossil fuels and work together toward a cleaner, greener future.”
Such entreaties, thus far, have been ignored. Both the Mets and the Dodgers have balked at the idea of intentionally walking away from sponsorships worth millions. But activists in New York and Los Angeles are hoping that more public officials—and more fans—will step up to the plate and pressure the teams to do the right thing. As that baseball sage Yogi Berra astutely pointed out, “It ain’t over till it’s over.”
This column was originally posted on Money Trail, a new Substack site co-founded by Elliott Negin.