The very notion of a “military-industrial complex” linking giant defense contractors to powerful figures in Congress and the military was introduced on January 17, 1961, by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in his farewell address to Congress and the American people. In that Cold War moment, in response to powerful foreign threats, he noted that “we have been compelled to create a permanent armaments industry of vast proportions.” Nevertheless, he added, using the phrase for the first time, “we must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military-industrial complex. The potential for the disastrous rise of misplaced power exists and will persist.”
Ever since, debate over the MIC’s accumulating power has roiled American politics. A number of politicians and prominent public figures have portrayed U.S. entry into a catastrophic series of foreign wars — in Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Iraq, Afghanistan, and elsewhere — as a consequence of that complex’s undue influence on policymaking. No such claims and complaints, however, have ever succeeded in loosening the MIC’s iron grip on Pentagon arms procurement. This year’s record defense budget of approximately $850 billion includes $143.2 billion for research and development and another $167.5 billion for the procurement of weaponry. That $311 billion, most of which will be funneled to those giant defense firms, exceeds the total amount spent on defense by every other country on Earth.
Over time, the competition for billion-dollar Pentagon contracts has led to a winnowing of the MIC ecosystem, resulting in the dominance of a few major industrial behemoths. In 2024, just five companies — Lockheed Martin (with $64.7 billion in defense revenues), RTX (formerly Raytheon, with $40.6 billion), Northrop Grumman ($35.2 billion), General Dynamics ($33.7 billion), and Boeing ($32.7 billion) — claimed the vast bulk of Pentagon contracts. (Anduril and General Atomics didn’t even appear on a list of the top 100 contract recipients.)
Typically, these companies are the lead, or “prime,” contractors for major weapons systems that the Pentagon keeps buying year after year. Lockheed Martin, for example, is the prime contractor for the Air Force’s top-priority F-35 stealth fighter (a plane that has often proved distinctly disappointing in operation); Northrop Grumman is building the B-21 stealth bomber; Boeing produces the F-15EX combat jet; and General Dynamics makes the Navy’s Los Angeles-class attack submarines. “Big-ticket” items like these are usually purchased in substantial numbers over many years, ensuring steady profits for their producers. When the initial buys of such systems seem to be nearing completion, their producers usually generate new or upgraded versions of the same weapons, while employing their powerful lobbying arms in Washington to convince Congress to fund the new designs.
Over the years, non-governmental organizations like the National Priorities Project and the Friends Committee on National Legislation have heroically tried to persuade lawmakers to resist the MIC’s lobbying efforts and reduce military spending, but without noticeable success. Now, however, a new force — Silicon Valley startup culture — has entered the fray, and the military-industrial complex equation is suddenly changing dramatically.
Along Came Anduril
Consider Anduril Industries, one of two under-the-radar companies that left three MIC heavyweights in the dust last April by winning the contract to build a prototype of the Collaborative Combat Aircraft. Anduril (named after the sword carried by Aragorn in J.R.R. Tolkien’s The Lord of the Rings) was founded in 2017 by Palmer Luckey, a virtual-reality headset designer, with the goal of incorporating artificial intelligence into novel weapons systems. He was supported in that effort by prominent Silicon Valley investors, including Peter Thiel of the Founders Fund and the head of another defense-oriented startup, Palantir (a name also derived from The Lord of the Rings).
From the start, Luckey and his associates sought to shoulder aside traditional defense contractors to make room for their high-tech startups. Those two companies and other new-fledged tech firms often found themselves frozen out of major Pentagon contracts that had long been written to favor the MIC giants with their bevies of lawyers and mastery of government paperwork. In 2016, Palantir even sued the U.S. Army for refusing to consider it for a large data-processing contract and later prevailed in court, opening the door for future Department of Defense awards.
In addition to its aggressive legal stance, Anduril has also gained notoriety thanks to the outspokenness of its founder, Palmer Luckey. Whereas other corporate leaders were usually restrained in their language when discussing Department of Defense operations, Luckey openly criticized the Pentagon’s inbred preference for working with traditional defense contractors at the expense of investments in the advanced technologies he believes are needed to overpower China and Russia in some future conflict.
Such technology, he insisted, was only available from the commercial tech industry. “The largest defense contractors are staffed with patriots who nevertheless do not have the software expertise or business model to build the technology we need,” Luckey and his top associates claimed in their 2022 Mission Document. “These companies work slowly, while the best [software] engineers relish working at speed. And the software engineering talent who can build faster than our adversaries resides in the commercial sector, not at large defense primes.”
To overcome obstacles to military modernization, Luckey argued, the government needed to loosen its contracting rules and make it easier for defense startups and software companies to do business with the Pentagon. “We need defense companies that are fast. That won’t happen simply by wishing it to be so: it will only happen if companies are incentivized to move” by far more permissive Pentagon policies.
Buttressed by such arguments, as well as the influence of key figures like Thiel, Anduril began to secure modest but strategic contracts from the military and the Department of Homeland Security. In 2019, it received a small Marine Corps contract to install AI-enabled perimeter surveillance systems at bases in Japan and the United States. A year later, it won a five-year, $25 million contract to build surveillance towers on the U.S.-Mexican border for Customs and Border Protection (CBP). In September 2020, it also received a $36 million CBP contract to build additional sentry towers along that border.
After that, bigger awards began to roll in. In February 2023, the Department of Defense started buying Anduril’s Altius-600 surveillance/attack drone for delivery to the Ukrainian military and, last September, the Army announced that it would purchase its Ghost-X drone for battlefield surveillance operations. Anduril is also now one of four companies selected by the Air Force to develop prototypes for its proposed Enterprise Test Vehicle, a medium-sized drone intended to launch salvos of smaller surveillance and attack drones.
Anduril’s success in winning ever-larger Pentagon contracts has attracted the interest of wealthy investors looking for opportunities to profit from the expected growth of defense-oriented startups. In July 2020, it received fresh investments of $200 million from Thiel’s Founders Fund and prominent Silicon Valley investor Andreessen Horowitz, raising the company’s valuation to nearly $2 billion. A year later, Anduril obtained another $450 million from those and other venture capital firms, bringing its estimated valuation to $4.5 billion (double what it had been in 2020). More finance capital has flowed into Anduril since then, spearheading a major drive by private investors to fuel the rise of defense startups — and profit from their growth as it materializes.
The Replicator Initiative
Along with its success in attracting big defense contracts and capital infusions, Anduril has succeeded in convincing many senior Pentagon officials of the need to reform the department’s contracting operations so as to make more room for defense startups and tech firms. On August 28, 2023, Deputy Secretary of Defense Kathleen Hicks, then the department’s second-highest official, announced the inauguration of the “Replicator” initiative, designed to speed the delivery of advanced weaponry to the armed forces.
“[Our] budgeting and bureaucratic processes are slow, cumbersome, and byzantine,” she acknowledged. To overcome such obstacles, she indicated, the Replicator initiative would cut through red tape and award contracts directly to startups for the rapid development and delivery of cutting-edge weaponry. “Our goal,” she declared, “is to seed, spark, and stoke the flames of innovation.”
As Hicks suggested, Replicator contracts would indeed be awarded in successive batches, or “tranches.” The first tranche, announced last May, included AeroVironment Switchblade 600 kamikaze drones (called that because they are supposed to crash into their intended targets, exploding on contact). Anduril was a triple winner in the second tranche, announced on November 13th. According to the Department of Defense, that batch included funding for the Army’s purchase of Ghost-X surveillance drones, the Marine Corps’ acquisition of Altius-600 kamikaze drones, and development of the Air Force’s Enterprise Test Vehicle, of which Anduril is one of four participating vendors.
Just as important, perhaps, was Hicks’ embrace of Palmer Luckey’s blueprint for reforming Pentagon purchasing. “The Replicator initiative is demonstrably reducing barriers to innovation, and delivering capabilities to warfighters at a rapid pace,” she affirmed in November. “We are creating opportunities for a broad range of traditional and nontraditional defense and technology companies… and we are building the capability to do that again and again.”
Enter the Trumpians
Kathleen Hicks stepped down as deputy secretary of defense on January 20th when Donald Trump reoccupied the White House, as did many of her top aides. Exactly how the incoming administration will address the issue of military procurement remains to be seen, but many in Trump’s inner circle, including Elon Musk and Vice President J.D. Vance, have strong ties to Silicon Valley and so are likely to favor Replicator-like policies.
Pete Hegseth, the former Fox News host who recently won confirmation as secretary of defense, has no background in weapons development and has said little about the topic. However, Trump’s choice as deputy secretary (and Hick’s replacement) is billionaire investor Stephen A. Feinberg who, as chief investment officer of Cerberus Capital Management, acquired the military startup Stratolaunch — suggesting that he might favor extending programs like Replicator.
In a sense, the Trump moment will fit past Washington patterns when it comes to the Pentagon in that the president and his Republican allies in Congress will undoubtedly push for a massive increase in military spending, despite the fact that the military budget is already at a staggering all-time high. Every arms producer is likely to profit from such a move, whether traditional prime contractors or Silicon Valley startups. If, however, defense spending is kept at current levels — in order to finance the tax cuts and other costly measures favored by Trump and the Republicans — fierce competition between the two versions of the military-industrial complex could easily arise again. That, in turn, might trigger divisions within Trump’s inner circle, pitting loyalists to the old MIC against adherents to the new one.
Most Republican lawmakers, who generally rely on contributions from the old MIC companies to finance their campaigns, are bound to support the major prime contractors in such a rivalry. But two of Trump’s key advisers, J.D. Vance and Elon Musk, could push him in the opposite direction. Vance, a former Silicon Valley functionary who reportedly became Trump’s running mate only after heavy lobbying by Peter Thiel and other tech billionaires, is likely to be encouraged by his former allies to steer more Pentagon contracts to Anduril, Palantir, and related companies. And that would hardly be surprising, since Vance’s private venture fund, Narya Capital (yes, another name derived from The Lord of the Rings!), has invested in Anduril and other military/space ventures.
Named by Trump to direct the as-yet-to-be-established Department of Government Efficiency, Elon Musk, like Anduril’s Palmer Luckey, fought the Department of Defense to obtain contracts for one of his companies, SpaceX, and has expressed deep contempt for the Pentagon’s traditional way of doing things. In particular, he has denigrated the costly, generally ill-performing Lockheed-made F-35 jet fighter at a time when AI-governed drones are becoming ever more capable. Despite that progress, as he wrote on X, the social media platform he now owns, “some idiots are still building manned fighter jets like the F-35.” In a subsequent post, he added that “manned fighter jets are obsolete in the age of drones anyway.”
His critique of the F-35 ruffled feathers at the Air Force and caused Lockheed’s stock to fall by more than 3%. “We are committed to delivering the world’s most advanced aircraft — the F-35 — and its unrivaled capabilities with the government and our industry partners,” Lockheed declared in response to Musk’s tweets. Over at the Pentagon, Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall had this to say: “I have a lot of respect for Elon Musk as an engineer. He’s not a warfighter, and he needs to learn a little bit more about the business, I think, before he makes such grand announcements as he did.” He then added, “I don’t see F-35 being replaced. We should continue to buy it, and we also should continue to upgrade it.”
President Trump has yet to indicate his stance on the F-35 or other high-priced items in the Pentagon’s budget lineup. He may (or may not) call for a slowdown in purchases of that plane and seek greater investment in other projects. Still, the divide exposed by Musk — between costly manned weapons made by traditional defense contractors and more affordable unmanned systems made by the likes of Anduril, General Atomics, and AeroVironment — is bound to widen in the years to come as the new version of the military-industrial complex only grows in wealth and power. How the old MIC will address such a threat to its primacy remains to be seen, but multibillion-dollar weapons companies are not likely to step aside without a fight. And that fight will likely divide the Trumpian universe.



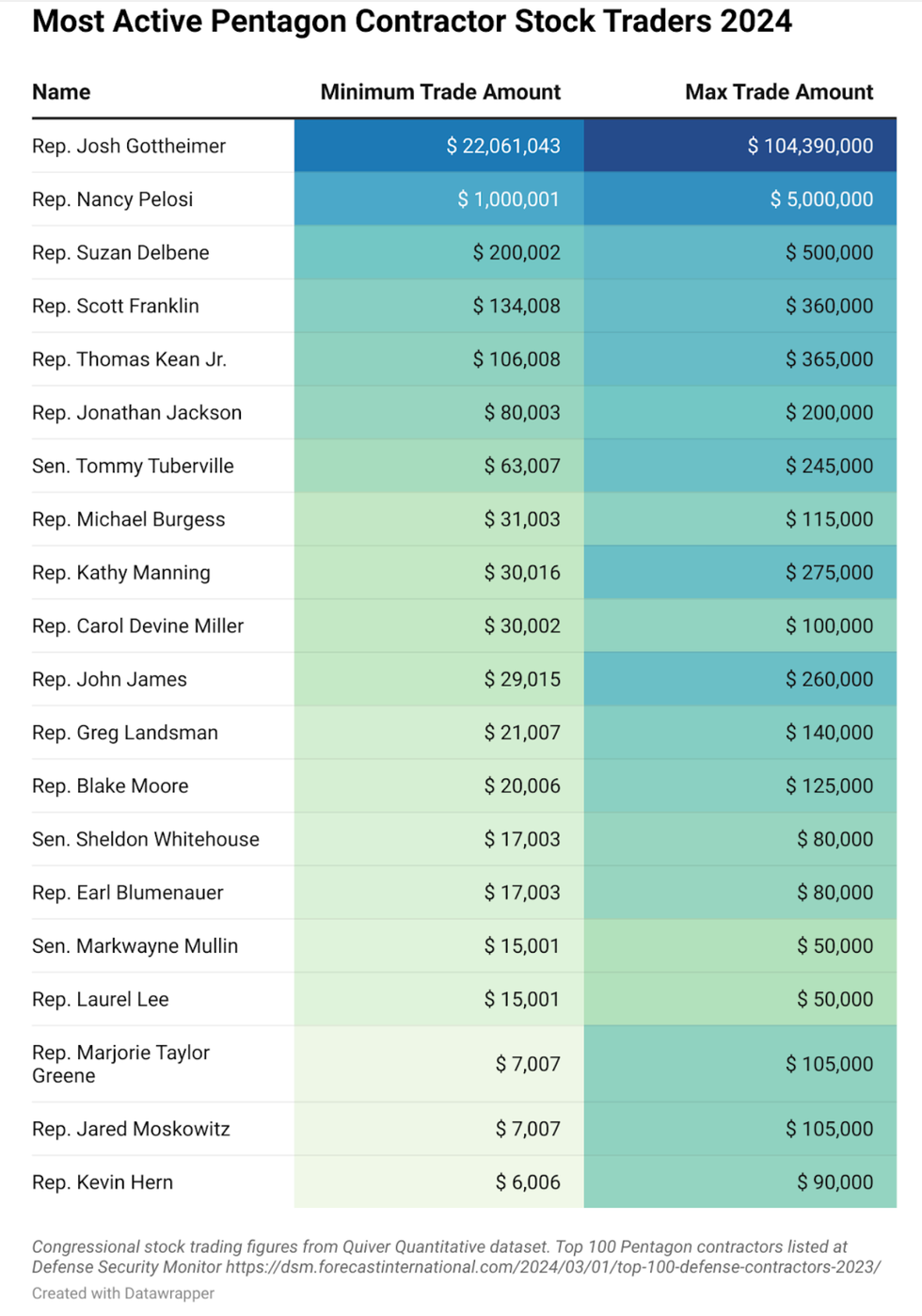 (Image: Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft/Datawrapper)
(Image: Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft/Datawrapper) 