Google-Owned YouTube Makes Millions From Channels Pushing Climate Disinformation: Analysis
"It's time for YouTube to step up, detox its platform, and protect the integrity of the fight against the climate crisis," said Ekō's campaign director.
Google-owned YouTube is again facing allegations of profiting from not enforcing its own ban on the monetization of climate misinformation, this time in a report published Friday amid legislative battles in Brazil over policies on the Amazon rainforest, Indigenous rights, and social media.
Google announced in October 2021 that for advertisers and publishers along with creators on its video platform YouTube, the company would "prohibit ads for, and monetization of, content that contradicts well-established scientific consensus around the existence and causes of climate change."
For four weeks, researchers with Ekō—a group formerly known as SumOfUs that works to curb the power of big corporations—reviewed 60 YouTube videos in English and Portuguese that contained disinformation and conspiracy theories about Amazon deforestation, Indigenous rights, and the climate emergency.
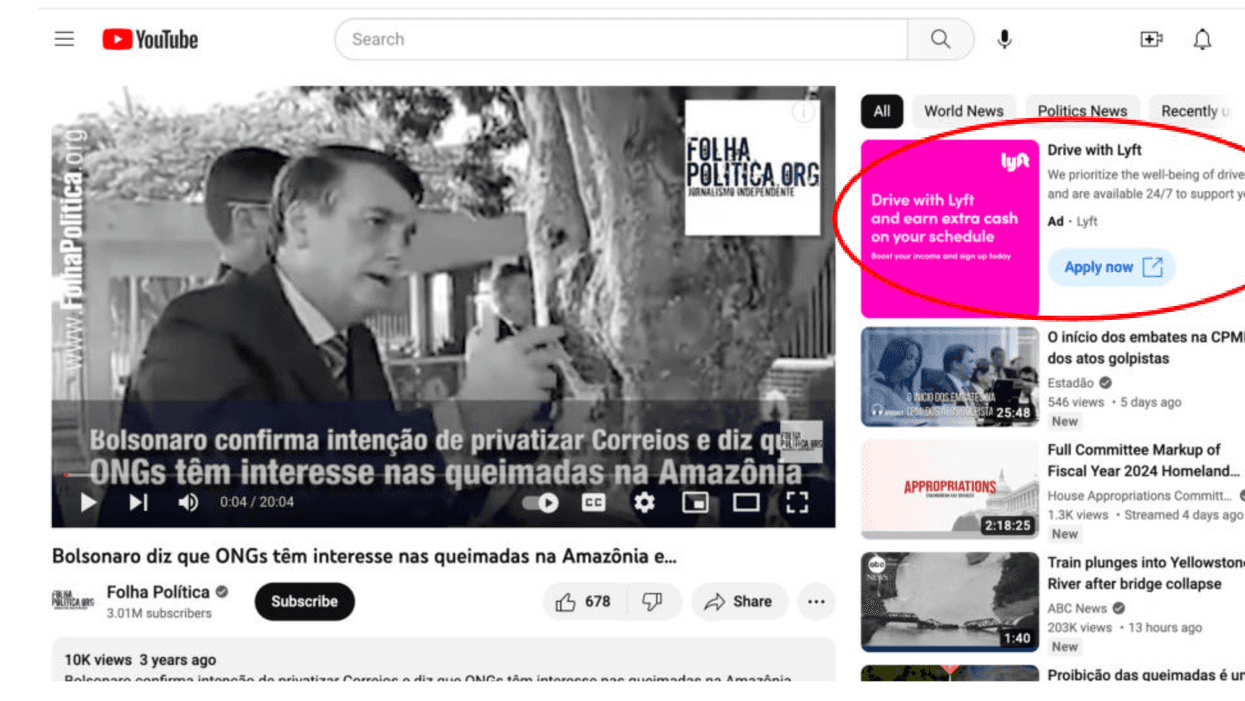
Over two-thirds of the videos were monetized, and Ekō identified more than 150 brands in the ads. Using a common industry tool, researchers estimated that the channels—which collectively had over 40 million subscribers and more than 5 million views—earn $636,000 to $10.1 million a year through monetization.
"The proliferation of disinformation and conspiracy theories are helping to derail efforts by the Lula administration to advance policy agendas around Amazon protection, Indigenous land rights, and social media regulation."
"Well-known Brazilian and global brands like Lyft, Calvin Klein, Budweiser, Panasonic, and Samsung, as well as environmental and human rights groups like Friends of the Earth U.K., UNICEF, and the Peace Corps, are appearing next to extreme climate denial content and conspiracy theories," the report states, "effectively pouring money into the pockets of conspiracy theorists and climate deniers."
"Ekō researchers found top-name apparel, electronics, and drink brands appearing next to videos suggesting actor Leonardo DiCaprio funded nongovernmental organizations to commit arson in the Amazon," the publication continues. "Other false claims include that the rainforest is too humid to catch fire, and that manmade global warming is a lie."
"The proliferation of disinformation and conspiracy theories are helping to derail efforts by the Lula administration to advance policy agendas around Amazon protection, Indigenous land rights, and social media regulation," the document adds, pushing for policy "that prevents platforms from monetizing and profiting from disinformation and lies that are subverting the legislative process."
In a statement Friday, Ekō campaign director Vicky Wyatt also demanded action from the company.
"While global warming, deforestation, and wildfires reach their highest levels ever recorded, YouTube's shameless greenwashing is exposed—with the company giving profits to climate deniers to the tune of millions," said Wyatt. "This is a clear slap in the face to the brands whose advertisements unknowingly support climate disinformation. It's time for YouTube to step up, detox its platform, and protect the integrity of the fight against the climate crisis."
Ekō's analysis follows a May report from Climate Action Against Disinformation (CAAD) for which researchers found 200 YouTube videos containing climate mis- and disinformation. The videos had a total of 73.8 million views and all had featured ads.
YouTube spokesperson Michael Aciman told Engadget in response to those findings that the company is "constantly working" to remove content that violates its rules and welcomes third-party feedback to "help improve the accuracy of our enforcement over time."
"In 2021, we launched a new, industry-leading policy that explicitly prohibits ads from running on content promoting false claims about the existence and causes of climate change, which we designed in consultation with experts and authoritative sources on climate science," Aciman also said. "We do allow policy debate or discussions of climate-related initiatives, but when content crosses the line to climate change denial, we remove ads from serving on those videos.”
Meanwhile, Callum Hood, head of research at the Center for Countering Digital Hate, part of the CAAD coalition, said at the time that "despite Google's green grandstanding, its ads continue to fuel the climate denial industry."
"Whether it's taking cash to target users with climate disinformation, or running ads that make climate denial content profitable, the company is selling out," Hood added. "Tech companies make big promises on hate and misinformation because they know it's hard to see if they've kept them. We need to force Google to open up the black box of its advertising business."