

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
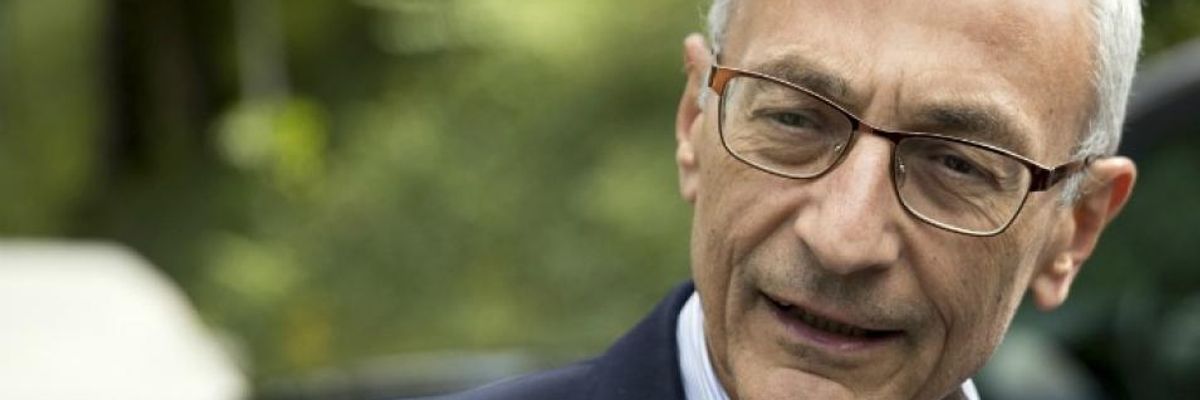

Emails of John Podesta, chair of Hillary Clinton's 2016 presidential campaign, were given to Wikileaks which then published them in a series of releases during the general election against Donald Trump. (Photo: Andrew Harnik/AP)
The Democratic National Committee (DNC) filed a lawsuit Friday afternoon in a Manhattan federal court against the Russian Government, the Trump campaign and various individuals it alleges participated in the plot to hack its email servers and disseminate the contents as part of the 2016 election. The DNC also sued WikiLeaks for its role in publishing the hacked materials, though it does not allege that WikiLeaks participated in the hacking or even knew in advance about it; its sole role, according to the DNC's lawsuit, was publishing the hacked emails.
The DNC's suit, as it pertains to WikiLeaks, poses a grave threat to press freedom. The theory of the suit - that WikiLeaks is liable for damages it caused when it "willfully and intentionally disclosed" the DNC's communications (paragraph 183) - would mean that any media outlet that publishes misappropriated documents or emails (exactly what media outlets quite often do) could be sued by the entity or person about which they are reporting, or even theoretically prosecuted for it, or that any media outlet releasing an internal campaign memo is guilty of "economic espionage" (paragraph 170):


It is extremely common for media outlets to publish or report on materials that are stolen, hacked, or otherwise obtained in violation of the law. In October, 2016 - one month before the election - someone mailed a copy of Donald Trump's 1995 tax returns to the New York Times, which published parts of it even though it is illegal to disclose someone's tax returns without the taxpayer's permission; in March, 2017, MSNBC's Rachel Maddow did the same thing with Trump's 2005 tax returns.

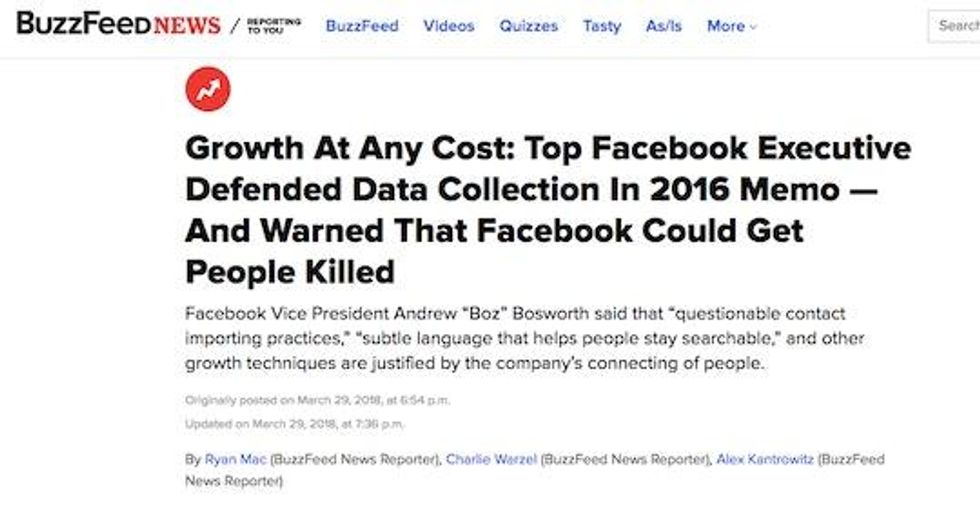
In April, 2016, the Washington Post obtained and published a confidential internal memo from the Trump campaign. Media outlets constantly publish private companies' internal documents. Just three weeks ago, BuzzFeed obtained and published a secret Facebook memo outlining the company's internal business strategies, the contents of which were covered by most major media outlets.
Some of the most important stories in contemporary journalism have come from media outlets obtaining and publishing materials that were taken without authorization or even in violation of the law. Both the New York Times and Washington Post published thousands of pages from the top secret Pentagon Papers after Daniel Ellsberg took them without authorization from the Pentagon - and they won the right to publish them in the U.S. Supreme Court.
Read the full article, with possible updates, at The Intercept.
Trump and Musk are on an unconstitutional rampage, aiming for virtually every corner of the federal government. These two right-wing billionaires are targeting nurses, scientists, teachers, daycare providers, judges, veterans, air traffic controllers, and nuclear safety inspectors. No one is safe. The food stamps program, Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid are next. It’s an unprecedented disaster and a five-alarm fire, but there will be a reckoning. The people did not vote for this. The American people do not want this dystopian hellscape that hides behind claims of “efficiency.” Still, in reality, it is all a giveaway to corporate interests and the libertarian dreams of far-right oligarchs like Musk. Common Dreams is playing a vital role by reporting day and night on this orgy of corruption and greed, as well as what everyday people can do to organize and fight back. As a people-powered nonprofit news outlet, we cover issues the corporate media never will, but we can only continue with our readers’ support. |
The Democratic National Committee (DNC) filed a lawsuit Friday afternoon in a Manhattan federal court against the Russian Government, the Trump campaign and various individuals it alleges participated in the plot to hack its email servers and disseminate the contents as part of the 2016 election. The DNC also sued WikiLeaks for its role in publishing the hacked materials, though it does not allege that WikiLeaks participated in the hacking or even knew in advance about it; its sole role, according to the DNC's lawsuit, was publishing the hacked emails.
The DNC's suit, as it pertains to WikiLeaks, poses a grave threat to press freedom. The theory of the suit - that WikiLeaks is liable for damages it caused when it "willfully and intentionally disclosed" the DNC's communications (paragraph 183) - would mean that any media outlet that publishes misappropriated documents or emails (exactly what media outlets quite often do) could be sued by the entity or person about which they are reporting, or even theoretically prosecuted for it, or that any media outlet releasing an internal campaign memo is guilty of "economic espionage" (paragraph 170):


It is extremely common for media outlets to publish or report on materials that are stolen, hacked, or otherwise obtained in violation of the law. In October, 2016 - one month before the election - someone mailed a copy of Donald Trump's 1995 tax returns to the New York Times, which published parts of it even though it is illegal to disclose someone's tax returns without the taxpayer's permission; in March, 2017, MSNBC's Rachel Maddow did the same thing with Trump's 2005 tax returns.

In April, 2016, the Washington Post obtained and published a confidential internal memo from the Trump campaign. Media outlets constantly publish private companies' internal documents. Just three weeks ago, BuzzFeed obtained and published a secret Facebook memo outlining the company's internal business strategies, the contents of which were covered by most major media outlets.

Some of the most important stories in contemporary journalism have come from media outlets obtaining and publishing materials that were taken without authorization or even in violation of the law. Both the New York Times and Washington Post published thousands of pages from the top secret Pentagon Papers after Daniel Ellsberg took them without authorization from the Pentagon - and they won the right to publish them in the U.S. Supreme Court.
Read the full article, with possible updates, at The Intercept.
The Democratic National Committee (DNC) filed a lawsuit Friday afternoon in a Manhattan federal court against the Russian Government, the Trump campaign and various individuals it alleges participated in the plot to hack its email servers and disseminate the contents as part of the 2016 election. The DNC also sued WikiLeaks for its role in publishing the hacked materials, though it does not allege that WikiLeaks participated in the hacking or even knew in advance about it; its sole role, according to the DNC's lawsuit, was publishing the hacked emails.
The DNC's suit, as it pertains to WikiLeaks, poses a grave threat to press freedom. The theory of the suit - that WikiLeaks is liable for damages it caused when it "willfully and intentionally disclosed" the DNC's communications (paragraph 183) - would mean that any media outlet that publishes misappropriated documents or emails (exactly what media outlets quite often do) could be sued by the entity or person about which they are reporting, or even theoretically prosecuted for it, or that any media outlet releasing an internal campaign memo is guilty of "economic espionage" (paragraph 170):


It is extremely common for media outlets to publish or report on materials that are stolen, hacked, or otherwise obtained in violation of the law. In October, 2016 - one month before the election - someone mailed a copy of Donald Trump's 1995 tax returns to the New York Times, which published parts of it even though it is illegal to disclose someone's tax returns without the taxpayer's permission; in March, 2017, MSNBC's Rachel Maddow did the same thing with Trump's 2005 tax returns.

In April, 2016, the Washington Post obtained and published a confidential internal memo from the Trump campaign. Media outlets constantly publish private companies' internal documents. Just three weeks ago, BuzzFeed obtained and published a secret Facebook memo outlining the company's internal business strategies, the contents of which were covered by most major media outlets.

Some of the most important stories in contemporary journalism have come from media outlets obtaining and publishing materials that were taken without authorization or even in violation of the law. Both the New York Times and Washington Post published thousands of pages from the top secret Pentagon Papers after Daniel Ellsberg took them without authorization from the Pentagon - and they won the right to publish them in the U.S. Supreme Court.
Read the full article, with possible updates, at The Intercept.