

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
Toxic air pollution poses an "enormous" risk to children worldwide, according to a new report from UNICEF released Monday.
In fact, the analysis finds that indoor and outdoor air pollution is a major contributing factor in the deaths of around 600,000 children under age five every year, with almost one in seven of the world's children--300 million--living in places where ultra-fine particulate matter in the air exceeds international guidelines by at least six times.
With "[m]any of these children...already disadvantaged by poverty and deprivation," the report states, "[a]ir pollution is yet another threat to their health and well-being--and yet another way in which the world is letting them down."
The UNICEF report, entitled Clean Air for Children (pdf), used satellite imagery to come up with its findings, confirming "that around two billion children live in areas where outdoor air pollution, caused by factors such as vehicle emissions, heavy use of fossil fuels, dust, and burning of waste, exceeds minimum air quality guidelines set by the World Health Organization."
South Asia and Africa are the regions most starkly impacted, as visible in the map below:
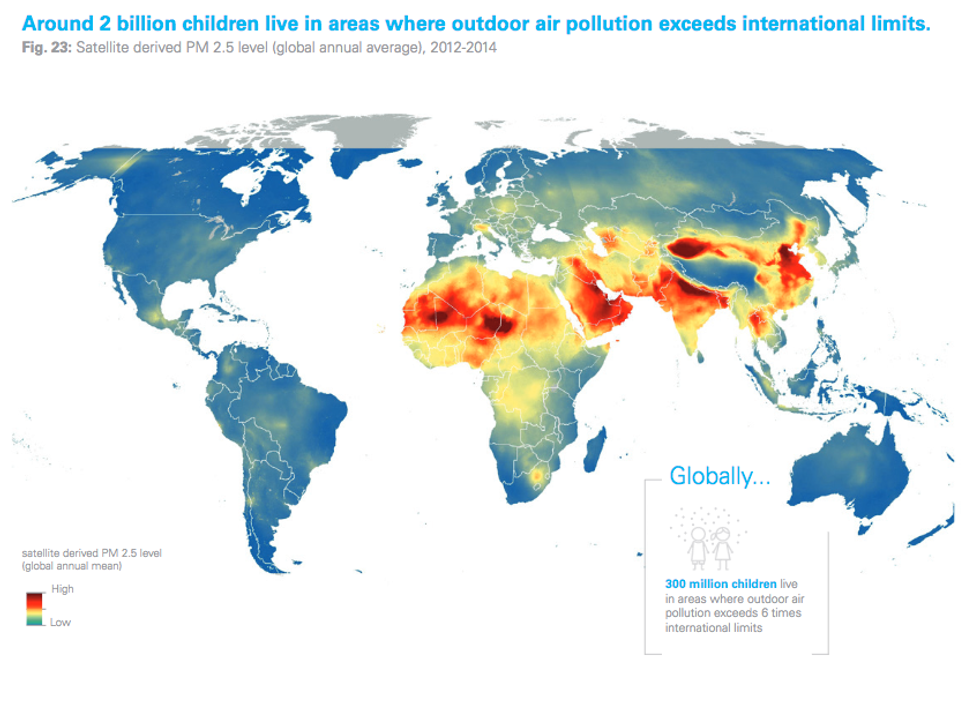
And the satellite imagery doesn't account for the estimated one billion children exposed to indoor air pollution, commonly caused by use of fuels like coal and wood for cooking and heating.
"Together, outdoor and indoor air pollution are directly linked to pneumonia and other respiratory diseases that account for almost one in 10 under-five deaths, making air pollution one of the leading dangers to children's health," reads a press statement from UNICEF.
In addition to those respiratory maladies, the study notes that air pollution can impair immune response and cognitive development in children, who it describes as "more physiologically vulnerable to air pollution than adults." A separate report from the World Health Organization (WHO), released last month, showed that more than 90 percent of people on the planet live in places where air pollution levels are dangerously high. The WHO called it a "public health emergency."
Released one week before the next U.N. climate conference, COP22, begins in Morocco, UNICEF's report contains several recommendations for policymakers at that gathering:
"We protect our children when we protect the quality of our air," said UNICEF executive director Anthony Lake. "Both are central to our future."
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
Toxic air pollution poses an "enormous" risk to children worldwide, according to a new report from UNICEF released Monday.
In fact, the analysis finds that indoor and outdoor air pollution is a major contributing factor in the deaths of around 600,000 children under age five every year, with almost one in seven of the world's children--300 million--living in places where ultra-fine particulate matter in the air exceeds international guidelines by at least six times.
With "[m]any of these children...already disadvantaged by poverty and deprivation," the report states, "[a]ir pollution is yet another threat to their health and well-being--and yet another way in which the world is letting them down."
The UNICEF report, entitled Clean Air for Children (pdf), used satellite imagery to come up with its findings, confirming "that around two billion children live in areas where outdoor air pollution, caused by factors such as vehicle emissions, heavy use of fossil fuels, dust, and burning of waste, exceeds minimum air quality guidelines set by the World Health Organization."
South Asia and Africa are the regions most starkly impacted, as visible in the map below:

And the satellite imagery doesn't account for the estimated one billion children exposed to indoor air pollution, commonly caused by use of fuels like coal and wood for cooking and heating.
"Together, outdoor and indoor air pollution are directly linked to pneumonia and other respiratory diseases that account for almost one in 10 under-five deaths, making air pollution one of the leading dangers to children's health," reads a press statement from UNICEF.
In addition to those respiratory maladies, the study notes that air pollution can impair immune response and cognitive development in children, who it describes as "more physiologically vulnerable to air pollution than adults." A separate report from the World Health Organization (WHO), released last month, showed that more than 90 percent of people on the planet live in places where air pollution levels are dangerously high. The WHO called it a "public health emergency."
Released one week before the next U.N. climate conference, COP22, begins in Morocco, UNICEF's report contains several recommendations for policymakers at that gathering:
"We protect our children when we protect the quality of our air," said UNICEF executive director Anthony Lake. "Both are central to our future."
Toxic air pollution poses an "enormous" risk to children worldwide, according to a new report from UNICEF released Monday.
In fact, the analysis finds that indoor and outdoor air pollution is a major contributing factor in the deaths of around 600,000 children under age five every year, with almost one in seven of the world's children--300 million--living in places where ultra-fine particulate matter in the air exceeds international guidelines by at least six times.
With "[m]any of these children...already disadvantaged by poverty and deprivation," the report states, "[a]ir pollution is yet another threat to their health and well-being--and yet another way in which the world is letting them down."
The UNICEF report, entitled Clean Air for Children (pdf), used satellite imagery to come up with its findings, confirming "that around two billion children live in areas where outdoor air pollution, caused by factors such as vehicle emissions, heavy use of fossil fuels, dust, and burning of waste, exceeds minimum air quality guidelines set by the World Health Organization."
South Asia and Africa are the regions most starkly impacted, as visible in the map below:

And the satellite imagery doesn't account for the estimated one billion children exposed to indoor air pollution, commonly caused by use of fuels like coal and wood for cooking and heating.
"Together, outdoor and indoor air pollution are directly linked to pneumonia and other respiratory diseases that account for almost one in 10 under-five deaths, making air pollution one of the leading dangers to children's health," reads a press statement from UNICEF.
In addition to those respiratory maladies, the study notes that air pollution can impair immune response and cognitive development in children, who it describes as "more physiologically vulnerable to air pollution than adults." A separate report from the World Health Organization (WHO), released last month, showed that more than 90 percent of people on the planet live in places where air pollution levels are dangerously high. The WHO called it a "public health emergency."
Released one week before the next U.N. climate conference, COP22, begins in Morocco, UNICEF's report contains several recommendations for policymakers at that gathering:
"We protect our children when we protect the quality of our air," said UNICEF executive director Anthony Lake. "Both are central to our future."