

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
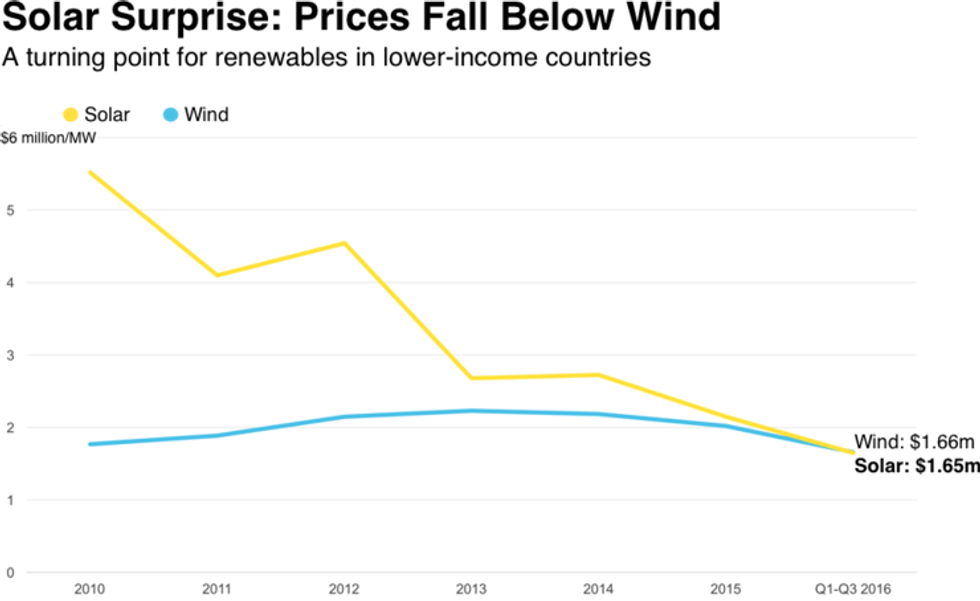
For the first time, solar power is becoming the cheapest form of electricity production in the world, according to new statistics from Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) released Thursday.
While unsubsidized solar has occasionally done better than coal and gas in individual projects, 2016 marked the first time that the renewable energy source has out-performed fossil fuels on a large scale--and new solar projects are also turning out to be cheaper than new wind power projects, BNEF reports in its new analysis, Climatescope.
The cost of solar in 58 developing nations dropped to about a third of 2010 levels, with China in particular adding a record number of solar projects. And as the Independent notes, solar "has proved a godsend for remote islands such as Ta'u, part of America Samoa, in the South Pacific."
In fact, Ta'u has been able to abandon the use of fossil fuels altogether and power itself almost entirely on renewable energy.
"Solar investment has gone from nothing--literally nothing--like five years ago to quite a lot," said Ethan Zindler, head of BNEF's U.S. policy analysis.
BNEF chairman Michael Liebreich also told investors this week that "[r]enewables are robustly entering the era of undercutting" fossil fuel prices.
Unsurprisingly, developing countries are at the forefront of this advancement, having invested in clean energy economies to stave off the catastrophic effects of climate change at a greater rate than wealthy nations.
"[F]or populations still relying on expensive kerosene generators, or who have no electricity at all, and for those living in the dangerous smog of thickly populated cities," Bloomberg reports, "the shift to renewables and increasingly to solar can't come soon enough."
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
For the first time, solar power is becoming the cheapest form of electricity production in the world, according to new statistics from Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) released Thursday.
While unsubsidized solar has occasionally done better than coal and gas in individual projects, 2016 marked the first time that the renewable energy source has out-performed fossil fuels on a large scale--and new solar projects are also turning out to be cheaper than new wind power projects, BNEF reports in its new analysis, Climatescope.
The cost of solar in 58 developing nations dropped to about a third of 2010 levels, with China in particular adding a record number of solar projects. And as the Independent notes, solar "has proved a godsend for remote islands such as Ta'u, part of America Samoa, in the South Pacific."
In fact, Ta'u has been able to abandon the use of fossil fuels altogether and power itself almost entirely on renewable energy.
"Solar investment has gone from nothing--literally nothing--like five years ago to quite a lot," said Ethan Zindler, head of BNEF's U.S. policy analysis.

BNEF chairman Michael Liebreich also told investors this week that "[r]enewables are robustly entering the era of undercutting" fossil fuel prices.
Unsurprisingly, developing countries are at the forefront of this advancement, having invested in clean energy economies to stave off the catastrophic effects of climate change at a greater rate than wealthy nations.
"[F]or populations still relying on expensive kerosene generators, or who have no electricity at all, and for those living in the dangerous smog of thickly populated cities," Bloomberg reports, "the shift to renewables and increasingly to solar can't come soon enough."
For the first time, solar power is becoming the cheapest form of electricity production in the world, according to new statistics from Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) released Thursday.
While unsubsidized solar has occasionally done better than coal and gas in individual projects, 2016 marked the first time that the renewable energy source has out-performed fossil fuels on a large scale--and new solar projects are also turning out to be cheaper than new wind power projects, BNEF reports in its new analysis, Climatescope.
The cost of solar in 58 developing nations dropped to about a third of 2010 levels, with China in particular adding a record number of solar projects. And as the Independent notes, solar "has proved a godsend for remote islands such as Ta'u, part of America Samoa, in the South Pacific."
In fact, Ta'u has been able to abandon the use of fossil fuels altogether and power itself almost entirely on renewable energy.
"Solar investment has gone from nothing--literally nothing--like five years ago to quite a lot," said Ethan Zindler, head of BNEF's U.S. policy analysis.

BNEF chairman Michael Liebreich also told investors this week that "[r]enewables are robustly entering the era of undercutting" fossil fuel prices.
Unsurprisingly, developing countries are at the forefront of this advancement, having invested in clean energy economies to stave off the catastrophic effects of climate change at a greater rate than wealthy nations.
"[F]or populations still relying on expensive kerosene generators, or who have no electricity at all, and for those living in the dangerous smog of thickly populated cities," Bloomberg reports, "the shift to renewables and increasingly to solar can't come soon enough."